53
ingress port belongs to, this packet will be dropped. When the VLAN-tagged packets are
forwarded by the Tagged port, its VLAN tag will not be changed.
¾ PVID
PVID (Port VLAN ID) is the default VID of the port. When the switch receives an un-VLAN-tagged
packet, it will add a VLAN tag to the packet according to the PVID of its received port and forward
the packets.
When creating VLANs, the PVID of each port, indicating the default VLAN to which the port
belongs, is an important parameter with the following two purposes:
(1) When the switch receives an un-VLAN-tagged packet, it will add a VLAN tag to the packet
according to the PVID of its received port
(2) PVID determines the default broadcast domain of the port, i.e. when the port receives UL
packets or broadcast packets, the port will broadcast the packets in its default VLAN.
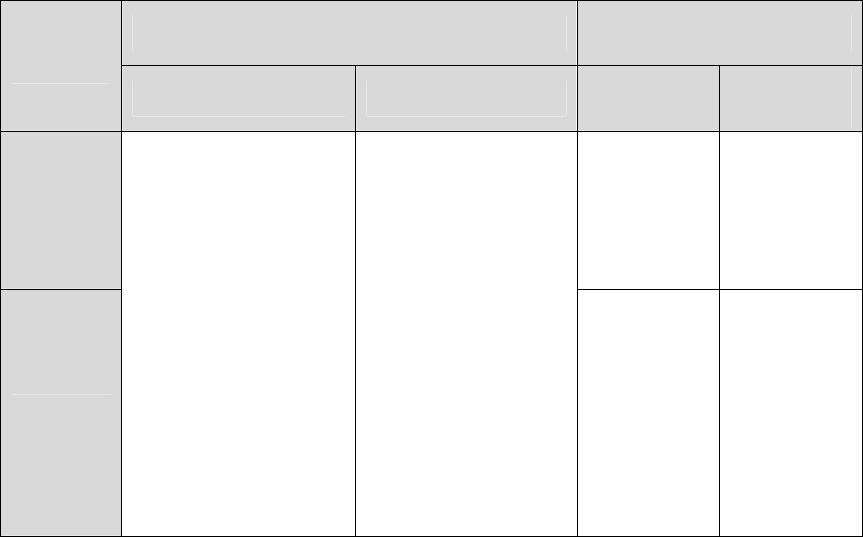
Different packets, tagged or untagged, will be processed in different ways, after being received by
ports of different link types, which is illustrated in the following table.
Receiving Packets Forwarding Packets
Port Type
Untagged Packets Tagged Packets
Untagged
Packets
Tagged
Packets
Untagged
The packet
will be
forwarded
unchanged.
The packet
will be
forwarded
after
removing its
VLAN tag
Tagged
When untagged
packets are received,
the port will add the
default VLAN tag, i.e.
the PVID of the
ingress port, to the
packets.
If the VID of packet is
allowed by the port,
the packet will be
received.
If the VID of packet is
forbidden by the port,
the packet will be
dropped.
The packet
will be
forwarded
with the
PVID of
egress port
as its VLAN
tag.
The packet
will be
forwarded
with its
current
VLAN tag.
Table 6-1 Relationship between Port Types and VLAN Packets Processing
IEEE 802.1Q VLAN function is implemented on the VLAN Config pages.
6.1.1 VLAN Config
On this page, you can configure the 802.1Q VLAN and its ports.
Choose the menu VLAN→802.1Q VLAN→VLAN Config to load the following page.


















