32 CHAPTER 4: CONFIGURING THE SWITCH
Switch will automatically connect at 1000Mbps, pro-
viding the connected device also supports this speed.
1000Mbps connections are always full-duplex.
Half-duplex connections are only available for
10Mbps and 100Mbps settings.
CAUTION: Before manually setting a port to
full-duplex, verify that the device connected to the
port is also manually set to the same speed and
duplex setting. If connecting link partners are left to
autonegotiate for a link manually set on this switch to
full-duplex, they will always negotiate to half-duplex,
resulting in a duplex mismatch. This can result in a
significant reduction in network performance. If you
are unsure of how to configure the speed/duplex set-
ting, simply enable autonegotiation for the port.
You cannot modify the speed/duplex settings of ports
that are members of a trunk or aggregated link.
Supported SFP transceivers only operate at 1000Mbps
full-duplex. Inserting an SFP transceiver into a gigabit
port disables the corresponding RJ-45 port, even if no
fiber cable is inserted.
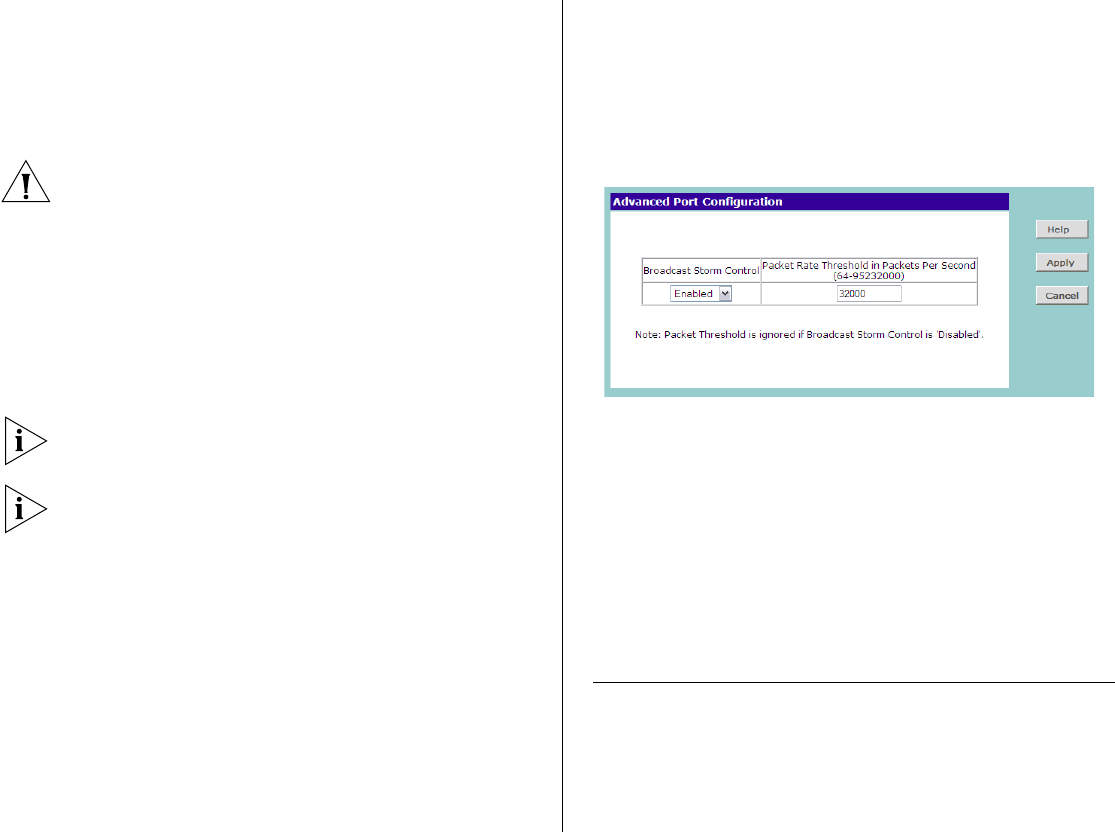
Advanced Port Configuration
Use the Advanced Port Configuration tab to set the
Switch’s broadcast storm control and threshold limits.
A broadcast storm is an incorrect packet sent out on a
network that causes most hosts to respond all at
once, typically with wrong answers that start the pro-
cess over again. Broadcast storms use substantial net-
work bandwidth and may cause network time-outs.
Advanced settings include:
■ Broadcast Storm Control – Enables and disables
broadcast storm control
■ Packet Rate Threshold – Sets the broadcast storm
threshold (64 to 95232000 bytes per packet)
Figure 13 Advanced Port Configuration Screen
Default Port Settings
If you do not configure the Switch’s port settings, the
ports will use the following default settings:
■ All ports are enabled
■ Autonegotiation is enabled
■ Flow control is enabled
■ All ports are set to priority zero
Configuring VLANs
You can use the Switch to create VLANs to organize
any group of ports into separate broadcast domains.
VLANs confine broadcast traffic to the originating
group and help eliminate broadcast storms in large


















