Campus Wireless Networks Validated Reference Design Version 3.3 | Design Guide Mobility Controller Configuration | 43
Using RADIUS and a WPA2 protected connection as an example, authentication occurs using 802.1X.
The Mobility Controller forwards the request to the RADIUS server who performs the actual
authentication and sends a response to the Mobility Controller. Once authentication completes
successfully, encryption keys are passed to the Mobility Controller from the RADIUS server, along with
the user’s access policies. The Mobility Controller then completes the role derivation process and adds
the new user, along with all the relevant state information, into the active user database and completes
the authentication process. A security context is created, and for encrypted links, key exchange occurs
where all traffic is now encrypted.
If the user already exists in the active user database and is now attempting to associate to a new AP, the
Mobility Controller will understand that an active user has moved, will restore the user’s connectivity
state and initiate mobility processing.
ArubaOS uniquely supports AAA FastConnect™, which allows the encrypted portions of 802.1x
authentication exchanges to be terminated on the Mobility Controller where Aruba’s hardware
encryption engine dramatically increases scalability and performance. Supported for PEAP-
MSCHAPv2, PEAP-GTC, and EAP-TLS, AAA FastConnect™ removes the requirement for external
authentication servers to be 802.1x-capable and increases authentication server scalability by
permitting several hundreds of authentication requests per second to be processed.
arun_056
WLAN
switch
1
5
34
3
AP
L2/L3
switch
Corporate
backbone
RADIUS
server
2
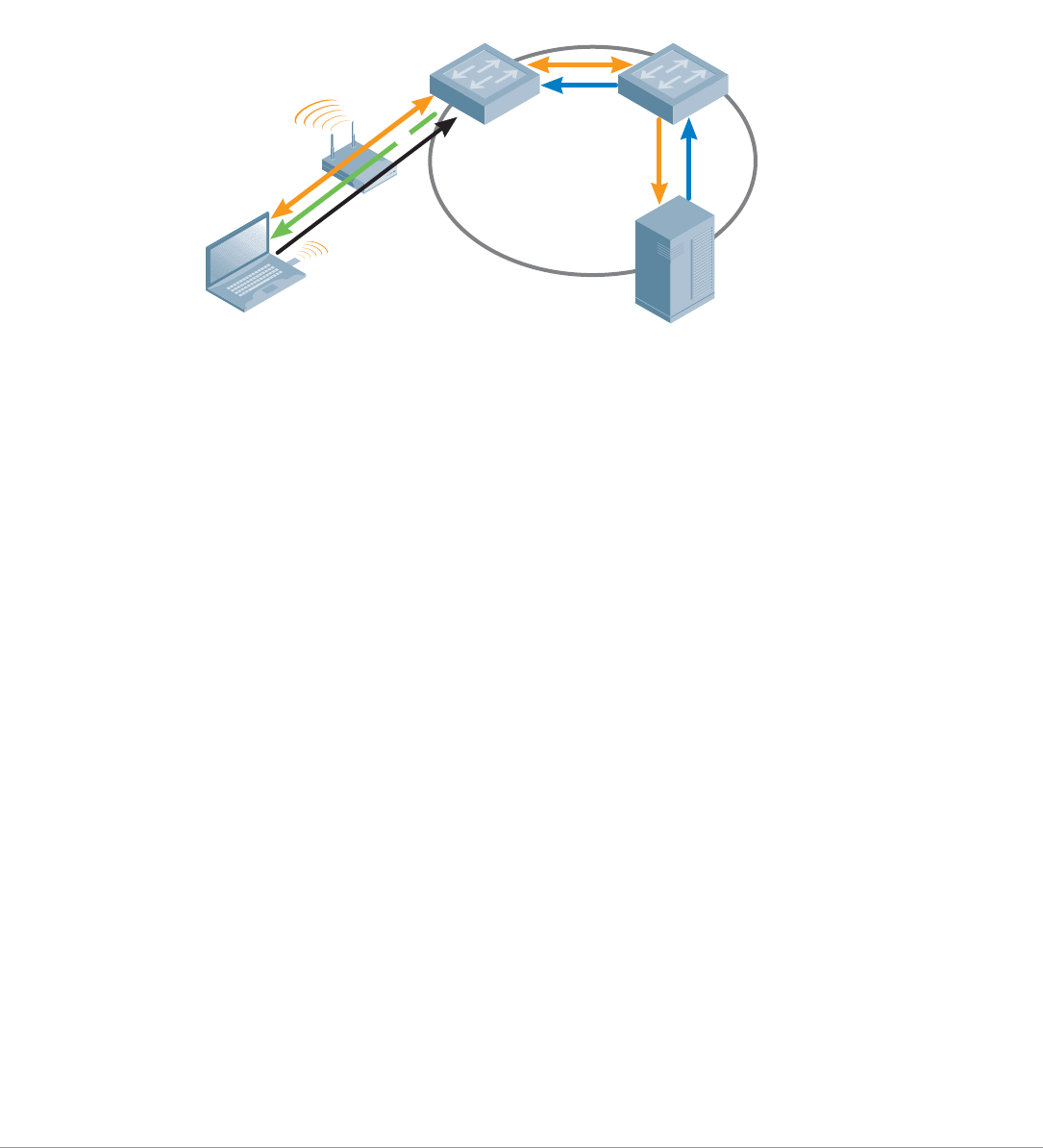
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
Client sends 802.11 association request that is
automatically forwarded by the AP to the WLAN switch
WLAN switch responds with association acknowledgement
Client and WLAN switch start 802.1X authentication
conversation along with RADIUS server
Encryption keys passed to the WLAN switch, and user derives
own encryption keys, begins sending encrypted data
WLAN switch decrypts data, processes packets, applies
services and forwards packets based on .11 MAC