8 | Aruba’s User-Centric Network Architecture Campus Wireless Networks Validated Reference Design Version 3.3 | Design Guide
Introducing Aruba’s User-Centric Network
In recent years, controller-based wireless switch architectures have been widely adopted to overcome
the limitations of the autonomous AP. The Aruba centralized WLAN model shown below represents a
structured model for WLAN deployment and ongoing management using a holistic approach to build
enterprise WLANs that support user mobility without sacrificing security, manageability and scalability.
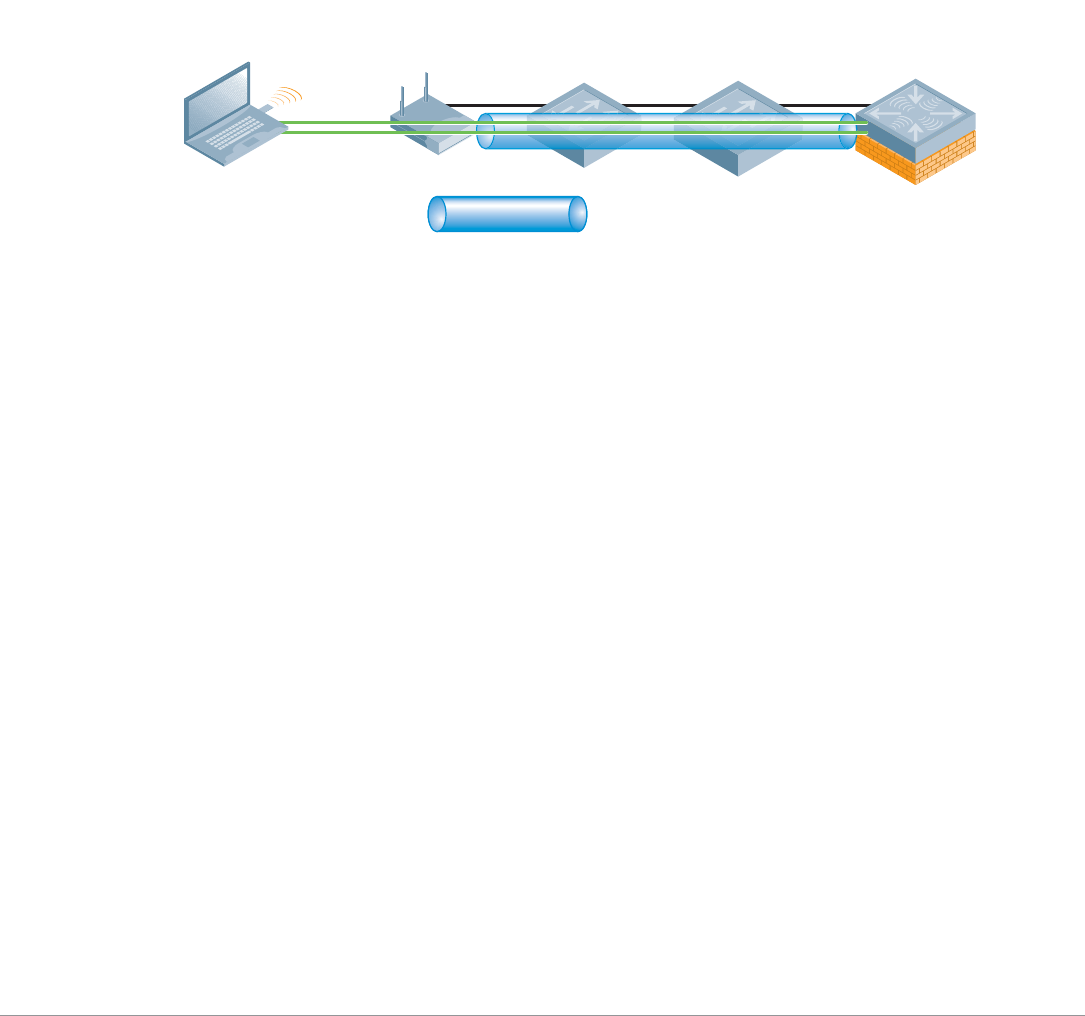
The Aruba User-Centric Network is an “overlay” network consisting of a centralized Mobility Controller
and thin APs that work together over an existing high-speed network. Most enterprise networks have
been engineered for high performance and high reliability, therefore, deploying the Aruba User-Centric
Network as an overlay will not adversely affect the investment and reliability of the existing network.
With this approach, a centralized appliance controls hundreds or thousands of network-attached radios
in a secure, reliable manner. This model represents a unified mobility solution integrating user mobility,
identity based security, remote access, and enterprise fixed mobile convergence (eFMC) solutions.
Centralized WLAN Model
In this system, the intelligence that once resided in autonomous APs is now integrated into a centralized
WLAN Mobility Controller designed for high-performance 802.11 packet processing, mobility and
security management. These controllers are typically deployed in secured data center environment or
distribution closets with redundant power and connectivity. APs are simplified and become network-
attached radios that perform only transceiver and air monitoring functions. These access points are
commonly referred to as “thin” APs. Connected to the Mobility Controller directly or over a layer 2/3
network by encrypted tunnels, they become extended access ports on the Mobility Controller directing
user traffic to the controller for processing; while providing visibility and control of the RF environment
to protect against intrusions (such as unauthorized users or rogue APs).
arun_031
Tunnel
Mobility
controller
Encryption
Thin AP
Client
termination
point


















