2
5.0 Features
The Buffalo AirStation Intelligent access point
provides the features necessary in today’s
business environment, with a high level of
reliability and security. Use of these features
along with VPN will allow the user to have
the highest security a WLAN can offer. For
minimum security measures Buffalo
recommends the use of 128bit WEP and
registering client MAC addresses in the
AirStation. Some of the noteworthy features
are shown below. Other features are listed
in Section 9.
5.1 Security Features
The WLM2-G54 model provides three levels
of security: authentication, privacy and access
authorization. The first level consists of
checking and issuing the user’s authentication
by EAP and 802.1x, similar to the Windows
XP authentication process.
The second is encrypting user’s data with
WEP, TKIP or MIC encryption algorithms.
Finally, granting the data access privilege only
after the user’s authentication is offered by
exchanging a specific key under the 802.1x
method.
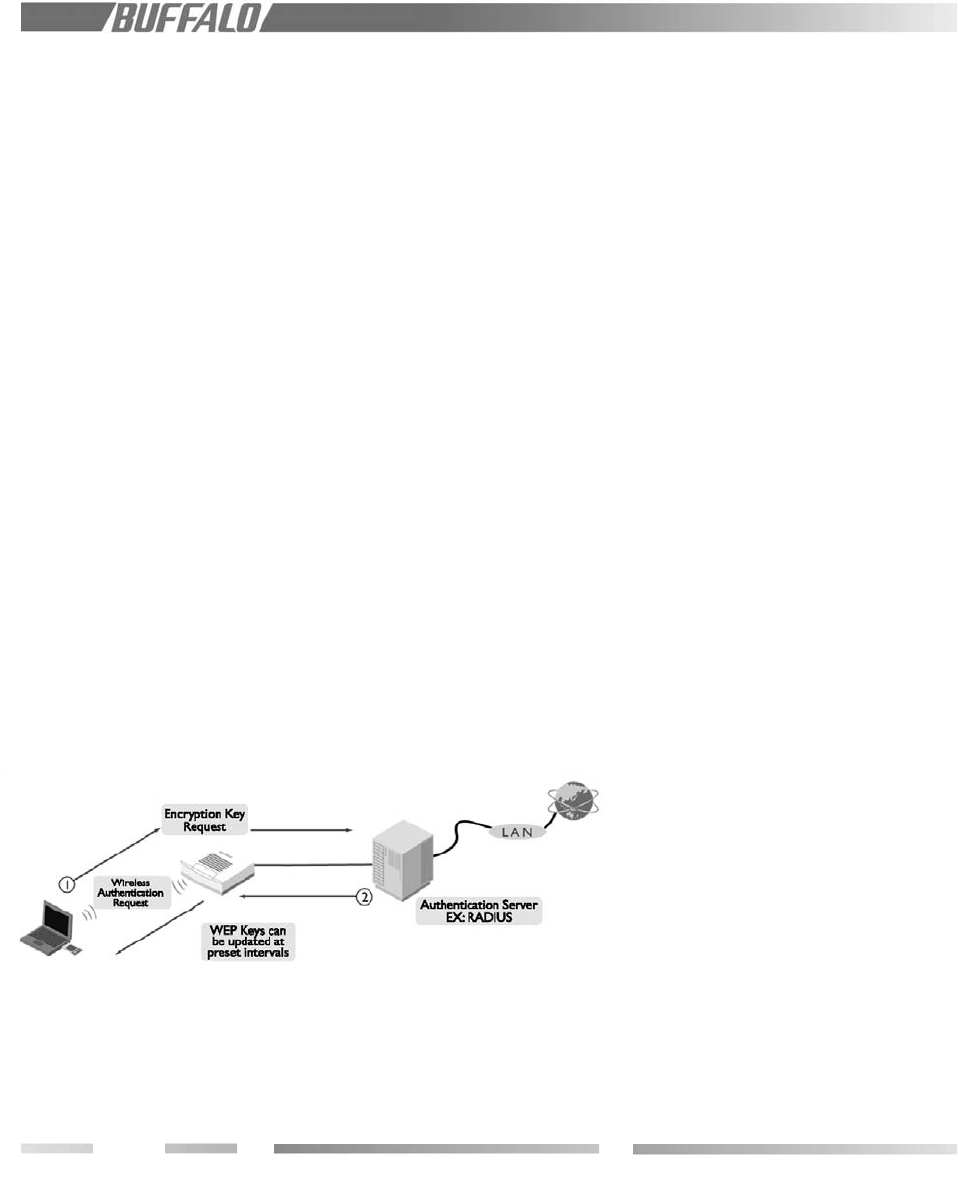
5.1.1 Authentication
The IEEE802.1x security method imposes
access port control at the access point level
for each user communication signal. The EAP
function in a client PC performs an authenti-
cation login to the authorization server, such
as RADIUS, through the WLM2-G54 access
point when the link is established and before
data transmission takes place.
EAP – Extensible Authentication Protocol is
a function in a client PC, which initiates the
authentication login to a network through an
AP such as the WLM2-G54. When the client
is approved and authenticated for a commu-
nication session, the client receives a unique
WEP key from a network security server such
as RADIUS.
802.1x – Known as .1x, this is the key
exchange standard used between a client and
an AP for the user’s authentication process.
Configuration for a large network is much
easier since individual WEP settings are no
longer required for each client. In addition,
access management is performed easily in the
RADIUS server environment, making this
feature valuable for network administration.
5.1.2 Privacy
Several encryption algorithms can be used to
mix with the data for protecting privacy. WEP
is the encryption method adopted in the
current WLAN industry. Because WEP was
found to be vulnerable, WEP will be replaced
with a more powerful Advanced Encryption
System (AES) in the future so that even
higher levels of security will be available.
Meanwhile, use of TKIP and MIC can be an
alternative to AES.
WEP – Wired Equivalent Privacy is a security
method for wireless networking using the
RC4 encryption algorithm. WEP consists of
two elements: an Initialization Vector (IV) of
24 bits that describes the packet header
information, and current data of 40 or 104
bits. For example, a 128bit WEP key means a
24bit IV plus a 104bit data encryption and
they are encrypted separately.