L-1
Appendix L. RF400/RF410 Average
Current Drain Calculations
For remote sites with tight power budgets due to solar or battery power
supplies, the following will help determine average current consumption. The
RF400/RF410’s average current drain is based on:
• Standby mode of RF400/RF410
• Data collection interval
• Number of data points collected
• “Time of inactivity to sleep” selection
STANDBY MODES
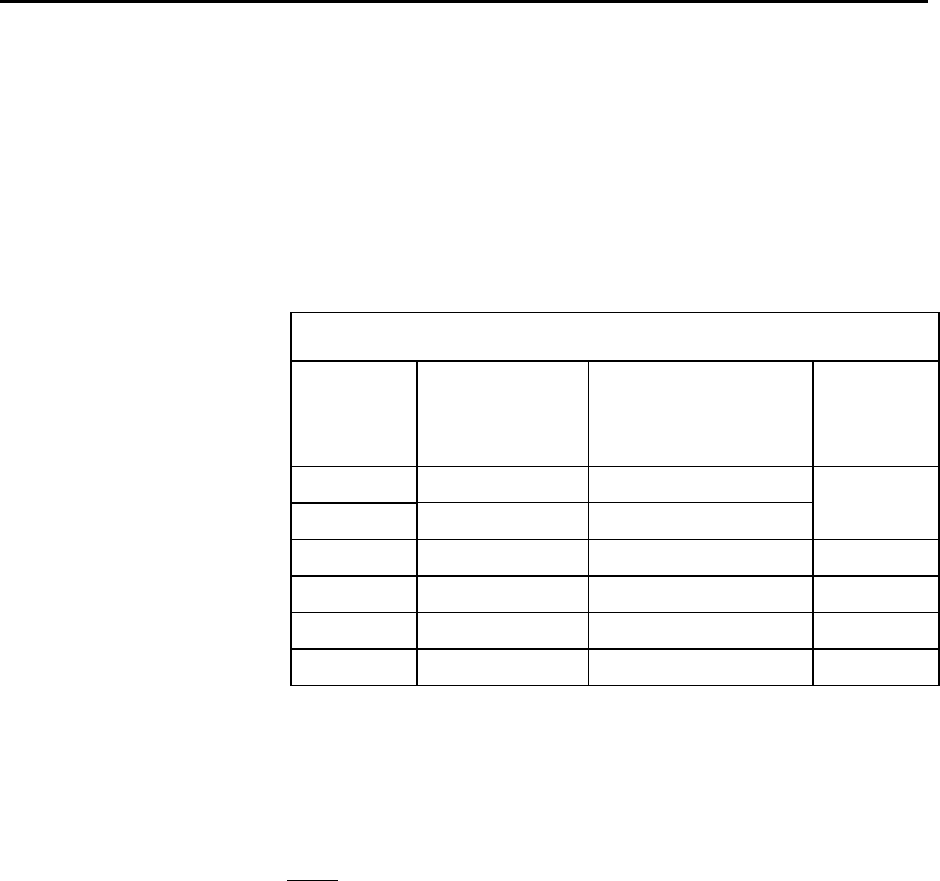
TABLE L-1. Advanced Setup Menu
STANDBY
MODE
STANDBY
AVG RECEIVE
CURRENT
(Is)
DEFAULT
TIME OF INACTIVITY
TO SLEEP
(sec)
“LONG
HEADER”
LENGTH
(L)
0
1
< 24 mA ----
3
2
< 4 mA 5
0 ms
700 ms
4
3
< 2 mA 5 1200 ms
5 < 1 mA 5 2200 ms
6 < 0.6 mA 5 4200 ms
7
4
< 0.4 mA 5 8200 ms
1
Standard Setup menu selection 1
2
Standard Setup menu selection 2
3
Standard Setup menu selection 3
4
Standard Setup menu selection 4
CALCULATIONS
BASE
The average current drain of a base RF400/RF410 configured for scheduled
collections has 5 contributors:
1) The STANDBY AVG RECEIVE CURRENT – Is
2) The average transmit current of LONG HEADER – Ih
3) The average transmit current of data request transmissions – Iq
4) The average receive current of data receptions – Ir
5) The average receive current of “time of inactivity to sleep” – Ii


















