14-3
Cisco IE 2000 Switch Software Configuration Guide
OL-25866-01
Chapter 14 Configuring Web-Based Authentication
Information About Configuring Web-Based Authentication
• Switch—Controls the physical access to the network based on the authentication status of the client.
The switch acts as an intermediary (proxy) between the client and the authentication server,
requesting identity information from the client, verifying that information with the authentication
server, and relaying a response to the client.
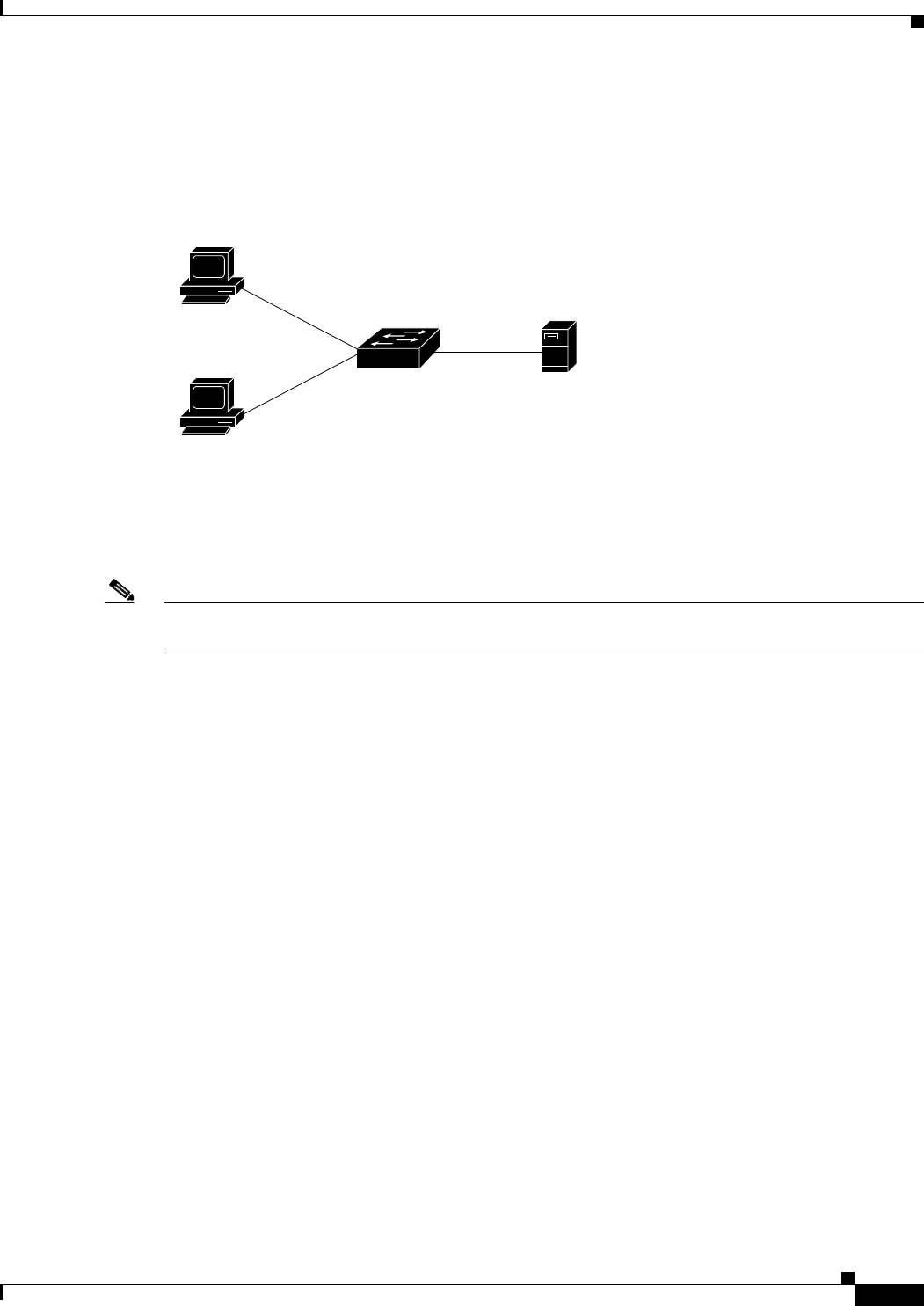
Figure 14-1 Web-Based Authentication Device Roles
Host Detection
The switch maintains an IP device tracking table to store information about detected hosts.
Note By default, the IP device tracking feature is disabled on a switch. You must enable the IP device tracking
feature to use web-based authentication.
For Layer 2 interfaces, web-based authentication detects IP hosts by using these mechanisms:
• ARP-based trigger—ARP redirect ACL allows web-based authentication to detect hosts with a static
IP address or a dynamic IP address.
• Dynamic ARP inspection
• DHCP snooping—Web-based authentication is notified when the switch creates a DHCP-binding
entry for the host.
Session Creation
When web-based authentication detects a new host, it creates a session as follows:
• Reviews the exception list.
If the host IP is included in the exception list, the policy from the exception list entry is applied, and
the session is established.
• Reviews for authorization bypass.
If the host IP is not on the exception list, web-based authentication sends a nonresponsive-host
(NRH) request to the server.
If the server response is access accepted, authorization is bypassed for this host. The session is
established.
• Sets up the HTTP intercept ACL.
Workstations
(clients)
Catalyst switch
or
Cisco Router
Authentication
server
(RADIUS)
79549