Feature Summary
2
Release 11.3(4)NA
List of Terms
CATV—Originally stood for Community Antenna Television. CATV now refers to any cable
(coaxial/fiber) based system that provides television services.
Cable modem—Any device that modulates and demodulates digital data onto a CATV plant.
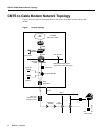
Cable router—A modular chassis-based router optimized for the data over CATV HFC
applications.
Channel—A specific frequency allocation and bandwidth. Downstream channels used for television
in the U. S. are 6 MHz wide.
CM—Cable modem.
CMTS—Cable Modem Termination System. Any DOCSIS compliant headend cable router, such as
the Cisco uBR7246.
Downstream—The set of frequencies used to send data from a headend to a subscriber.
Headend—Central distribution point for a CATV system. Video signals are received here from
satellite (either co-located or remote), frequency converted to the appropriate channels, combined
with locally originated signals, and rebroadcast onto the HFC plant. For a CATV data system, the
headend is the typical place to link between the HFC system and any external data networks.
HFC—Hybrid fiber-coaxial (cable). Older CATV systems were provisioned using only coaxial
cable. Modern systems use fiber transport from the headend to an optical node located in
neighborhood to reduce system noise. Coax runs from the node to the subscriber. The fiber plant is
generally a star configuration with all optical node fibers terminating at a headend. The coaxial cable
part of the system is generally a trunk-and-branch configuration.
Host—Any end-user computer system that connects to a network. The term host here refers to
computer systems connected to the LAN interface of the cable modem.
MAC layer—Media Access Control sublayer. Controls access by the cable modem to the CMTS
and to the upstream data slots.
MCNS—Multimedia Cable Network System Partners Ltd., a consortium of cable companies
representing the majority of homes in the U.S. and Canada who have decided to derive a standard
with the goal of having interoperable cable modems.
MSO—Multiple System Operator
QAM—Modulation scheme mostly used in the downstream direction (QAM-64, QAM-256).
QAM-16 is expected to be usable in the upstream direction. Numbers indicate number of code points
per symbol. The QAM rate or the number of points in the QAM constellation can be computed by 2
raised to the power of <number of bits/symbol>.
QPSK—Modulation scheme used in the upstream direction. Supports two data bits per symbol.
Subscriber Unit (SU)—An alternate term for cable modem. See cable modem.
Upstream—The set of frequencies used to send data from a subscriber to the headend.