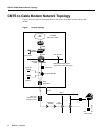
Connect to the Cable Modem
Troubleshooting Tips for the Cisco uBR904 Cable Modem 7
.
Connect to the Cable Modem
Telnet to the IP address assigned to the cable interface or Ethernet interface. If the interface is not
up, you need to access the Cisco IOS software via the RJ-45 console port, which is a physical port
on the back of the cable modem.
Because the MAC log file only holds a snapshot of 1023 entries at a time, you should try to display
the cable modem’s log file within 5 minutes of when the reset or problem occurs.
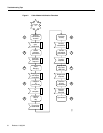
Table 1 Cable Modem Initialization Sequences and Events
Sequence Event Description
1 Scan for a downstream channel and
establish synchronization with the
headend Cisco uBR7246.
The cable modem acquires a downstream channel from the
headend, saves the last operational frequency in non-volatile
memory, and tries to reacquire the saved downstream
channel the next time a request is made.
An ideal downstream signal is one that synchronizes QAM
symbol timing, FEC framing, MPEG packetization, and
recognizes downstream sync MAC layer messages.
2 Obtain upsteam channel parameters. The cable modem waits for an upstream channel descriptor
messages (UCD) from the headend Cisco uBR7246. This is
done to retrieve transmission parameters for the upstream
channel.
3 Start ranging for power adjustments. The ranging process adjusts cable modem’s transmit power.
The cable modem performs ranging in stages, ranging state
1 and ranging state 2.
4 Establish IP connectivity. The cable modem invokes DHCP requests to obtain an IP
address, which is needed for IP connectivity. The DHCP
request also includes the name of a file that contains
additional configuration parameters, the TFTP server’s
address, and the Time of Day (TOD) server’s address.
5 Establish the time of day. The Cisco uBR904 cable modem accesses the TOD server
for the current date and time, which is used to create time
stamps for logged events (such as those displayed in the
MAC log file).
6 Establish security. Keys for privacy are exchanged between the cable modem
and the CMTS (the Cisco uBR7246 cable router).
7 Transfer operational parameters. After the DHCP and security operations are successful, the
cable modem downloads operational parameters from a
configuration file stored on a cable company’s TFTP server.
8 Perform registration. The cable modem registers with the headend
Cisco uBR7246. The cable modem is authorized to forward
traffic into the cable network after the cable modem is
initialized, authenticated, and configured.
Note The Cisco uBR904 cable modem supports baseline
privacy in Cisco IOS Release 11.3(5)NA and later.
9 Comply with baseline privacy. Link level encryption keys are exchanged between the
headend and the cable modem.
10 Enter the operational maintenance
state.
As soon as the cable modem is completely up and running,
it enters operational maintenance state.