www.cooperbussmann.com/BussmannWirelessResources
17
Cooper Bussmann BU-245U-E Wireless Ethernet & Device Server User Manual
CHAPTER 3 OPERATION
3.0 Start-up
“Access Point” Start-up (BU-245U-E-G)
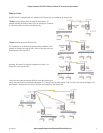
When an Access Point (AP) unit starts up it checks to see if the Channel selection is set to “Auto” and if so will scan all available channels, pick
the quietest then begin transmitting periodic messages, called beacons, if it is configured with a fixed channel it will immediately begins sending
beacons, on the configured channel.
Beacons include information that a Client may examine in order to identify if the Access Point is suitable for link establishment. Clients will only
attempt to establish a link with an Access Point whose beacon indicates a matching SSID. Access Points do not initiate link establishment.
“Access Point” Start-up (BU-245U-E-A)
If the modem is configured to use “DFS” then it will behave slightly different, as it needs to comply with DFS regulations.
When an Access Point starts up it will scan all available channels from the selected groups and then select the quietest similar to the
BU-245U-E-G. It will then go into a scan mode for 60 seconds where it listens for any Radar signals.
If a radar signal is detected it will flag the channel as being unavailable (Channel will stay unavailable for 30 minutes) and then pick another
random channel and go through the same scanning process until a radar free channel be comes available.
“Client” Start-up
When a Client powers up, it scans for beacons from Access Points. While a link is not established, the Client cyclically scans all available channels
for a suitable Access Point. The Client will attempt to establish a link with an Access Point only if it has matching SSID, Encryption method, etc.
and other compatible capabilities as indicated by the beacon. If more than one suitable Access Point is discovered, the client will attempt to
establish a link with the Access Point that has the strongest radio signal.
Link Establishment
Once a Client identifies a suitable Access Point for link establishment it attempts to establish a link using a two step process – “Authentication”
and “Association.” During Authentication the Client and Access Point check if their configurations permit them to establish a link. Once the Client
has been authenticated, it will then request an Association to establish a link.
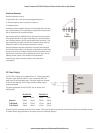
Status of the wireless link is indicated via the TX/LINK LED. For an Access Point, the TX/LINK LED will be OFF while no links have been estab-
lished. Once one or more links have been established, the TX/LINK LED is on GREEN. For a Client, the Link LED will reflect the connection status
to an Access Point. Link status is also displayed on the “Connectivity” page of the web interface.
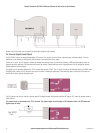
After the link is established, data may be transferred in both directions. The Access Point will act as a master-unit and will control the flow of data
to the Clients linked to it. Clients can only transmit data to the AP to which they are connected. When a Client transfers data to another Client, it
first transmits the data to the AP, which then forwards the data to the destined Client.
Presence of a “link” does not mean that the connected unit is authorized to communicate over radio. If the encryption
keys are incorrect between units in the same system, or a dissimilar encryption scheme is configured, the LINK led will
light, however data cannot be passed over the wireless network.
A maximum of 127 Clients may be linked to an Access Point.
How a Link Connection is Lost
The Access Point refreshes the link status with a Client every time a message is received from that Client. If nothing is received from a Client for a
period of 120 seconds, the Access Point sends a “link-check” message. If there is no response to the link-check a De-authenticate message is
sent and the link is dropped.
A Client monitors beacon messages from an Access Point to determine whether the link is still present. If the Client can no longer receive beacons
from the Access Point it assumes the AP is out-of-range and the link is dropped. Whenever a Client is not connected to an AP, it will cyclically
scan all available channels for a suitable AP.
3A1576Rev1.6