S1C6200/6200A CORE CPU MANUAL EPSON 11
2 MEMORY AND OPERATIONS
Hexadecimal operations will not always produce the correct result if performed in decimal mode.
Note that:
• An add instruction with carry (for example, ADC XH,i) which uses index registers XH, XL, YH and YL,
does not involve decimal correction even if it is performed in the decimal mode. This is because it uses
an 8-bit field for 4-bit data.
• The results of the compare instruction (CP) is not decimal-corrected, because the carry flag is ignored.
• The result of the register memory increment instruction (INC Mn) and decrement instruction (DEC Mn)
are not decimal-corrected.
2.3.2 A and B registers
The A and B registers are 4-bit general-purpose registers used as accumulators. They transfer data and
perform ALU operations with other registers, data memory and immediate data.
The data in A can be paired with that in B for use as an indirect jump address by the JPBA instruction.
2.4 Timing Generator
S1C6200/6200A instructions can be divided into three different types depending on the number of clock
cycles per instruction: 5, 7 or 12 clock cycles. The more complex the instruction, the more cycles it requires.
Note that the number of clock cycles determines the duration of instructions which, in turn, will affect any
timing performed in software.
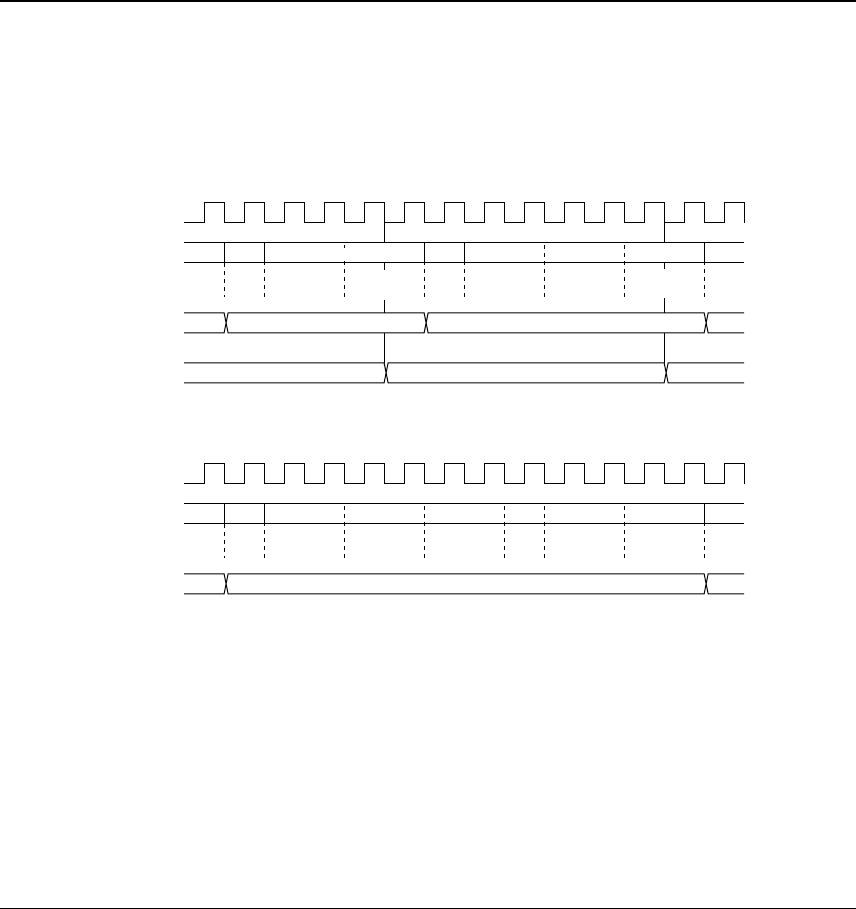
As shown in Figure 2.4.1, the first state of all instructions is a fetch cycle. This is followed by a number of
execute cycles.
Clock
Status
Instruction
register
Date
memory
Fetch ExecuteFetch
State
0
State
1
State
2
State
0
State
1
State
2
State
3
Execute
5-clock/7-clock instructions
Clock
Status
Instruction
register
Fetch
State
0
State
1
State
2
State
3
State
4
State
5
State
6
Execute
12-clock instructions
Fig. 2.4.1 Instruction execution timing
2.4.1 HALT and SLP (sleep) modes
HALT and SLP cause the CPU to store the return address on the stack and then stop. HALT will only stop
the CPU; the system clock will continue to run. SLP also stops the system clock, resulting in reduced power
consumption. The CPU can be restarted by an interrupt.
As interrupts are not automatically enabled by the execution of HALT or SLP, programs should always
enable interrupts before executing HALT or SLP, otherwise they will hang waiting for an interrupt.