C141-F037-02EN 5 - 15
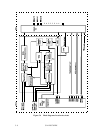
5.7.3 Data-side servo data format
Position
GapGap
5,067 µs
Gray code
Gap
Servo
mark
W/R recovery
Figure 5.7 Servo frame
5.7.4 Spindle motor control
The FC control MCU controls the senseless 3-phase spindle motor. It carries out start / normal rotation
control in accordance with commands from the FC unit.
(1) Activation
The FC control MCU carries out control of the spindle motor from the stopped condition to
normal rotation by the following sequence.
1) DSP intermittently supplies current between specific phases (e.g., phases U and V) to force a
fixed motor rotation position. This operation is called alignment.
2) In the next timing phase of 1) above, the DSP creates a rotating magnetic field. The motor
rotates from a low rotational frequency up to about 100 rpm. This is called synchronization
control.
3) When the motor reaches a high rotational frequency, a counterelectromotive voltage (back
EMF) is generated. This voltage tells the DSP the rotational frequency and angular position
of the motor. Using the rotation position detection data, the spindle controller supplies
current to the correct phase to rotate the motor. The MCU then detects the rotational
frequency, and the spindle controller accelerates the motor up to the steady-state angular
frequency.
(2) Rotational speed control mode
When the activation mode terminates, the rotational speed control mode starts. The MPU
controls the controller to maintain the detected rotational speed.