Chapter 3
Detailed Description
The Detailed Picture of Hardware Monitoring
69
Event Polling (in Detail)
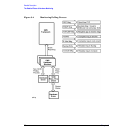
The following is the process used for gathering event information using polling. The polling process is
illustrated in Figure 3-4 on page 70.
1. At the interval defined by the polling value in the monitor configuration file, the monitor communicates
with all the devices it is currently monitoring. The monitor sends pass-thru commands to all SCSI
devices, and uses the appropriate protocol for other types of devices. The exact type and sequence of
communication used during a polling operation is monitor-specific.
2. Each device responds to the message from the monitor by returning data indicating its status. The
information returned in response to polling is not entered in the raw error log.
3. The monitor interprets the information from the device to determine if an event should be reported. If an
event should be reported, the monitor passes the event message to EMS.
4. EMS uses the current monitoring requests for the monitor to determine what action to take. Based on the
requests, the event is reported using the specified notification method(s).
FC-AL Hub and FC Switch Polling Processes
Unlike the other EMS hardware monitors, the FC-AL hub monitor and FC switch monitor use SNMP to
gather information from the hubs or switches they are monitoring. Using the hub or switch IP addresses
defined in the hub or switch configuration files, the monitor polls the devices at the defined polling interval
(60 minutes by default) using SNMP.
The reporting of events is handled in the same way as all other monitors. Event information gathered by the
hub and switch monitors does not get written to the raw error log, and the hub and switch monitors do not act
as a decoder for logtool.
PA Memory Monitor Polling
The memory monitor polling process uses different components to retrieve event information. The memory
monitor polling process is illustrated in Figure 3-5 on page 71.
1. At regular intervals (default 60 minutes) the memlogd daemon polls the memory hardware.
2. If a single-bit error is detected, memlogd uses the values from the memory configuration file to determine
the severity of the error, and then passes the appropriate event message to the memory monitor.
The error is also logged in memlog, which can read using logtool. All decoding of memory error messages
is performed by memlogd.
3. The memory monitor determines if the event should be reported. If the event should be reported, the
monitor passes the event message to Event Monitoring Service (EMS).
4. EMS uses the current monitoring requests for the memory monitor to determine what action to take.
Based on the requests, the event is reported using the specified notification method(s).