USER RESPONSIBLE FOR VERIFYING VERSION AND COMPLETENESS
OEM FUNCTIONAL SPECIFICATION ULTRASTAR XP (DFHC) SSA MODELS 1.12/2.25 GB - 1.0" HIGH
The time between the end of an operation, and when the next operation is issued is 50 msec, + / - a
random value of 0 to 50 msec, unless otherwise noted.
3.2.1 Sequential
No Seeks. The target LBA for all operations is the previous LBA + 64.
3.2.2 Random
All operations are to random LBAs. The average seek is an average weighted seek.
3.3 Command Execution Time
Command execution, or service, times are the sum of several Basic Components:
1. Seek
2. Latency
3. Command Execution Overhead
4. Data Transfer to/from Disk
5. Data Transfer to/from SSA Link
The impact or contribution of those Basic Components to Command Execution Time is a function of the
workload being sent to the drive and the environment in which the drive is being operated.
3.3.1 Basic Component Descriptions
Seek
The average time from the initiation of the seek, to the acknowledgement that the R/W head is
on the track that contains the first requested LBA. Values are population averages, and vary as
a function of operating conditions. The values used to determine Command Execution Times
for sequential commands is 0 milliseconds and the values for random commands are shown in
section 2.0, “Specifications” on page 11.
Latency
The average time required from the activation of the read/write hardware until the target sector
has rotated to the head and the read/write begins. This time is 1/2 of a revolution of the disk, or
4.17 milliseconds.
Command Execution Overhead
The average time added to the Command Execution Time due to the processing of the
command. It includes all time the drive spends not doing a disk operation or SSA link data
transfer.
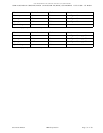
The following values are used when calculating the Command Execution Times.
Table 6. Overhead Values
A number of Initiator controlled factors affect Command Execution Overhead. These are exam-
ined separately in 3.4, “Approximating Performance for Different Environments” on page 43.
Workload Command Execution
Sequential Read .65 ms
Sequential Write 1.00 ms
Random Read .25 ms
Random Write .30 ms
Source filename=PERFORMIBM CorporationPage 40 of 87