89
MAC Address
MAC stands for media access control. A MAC address is the hardware address
of a device connected to a network. The MAC address is a unique identifier for a
device with an Ethernet interface. It is composed of two parts: 3 bytes of data
that corresponds to the manufacturer ID (unique for each manufacturer), plus 3
bytes that are often used as the product’s serial number.
NAT
A network address translator is defined by RFC 1631. It enables a LAN network
to use one set of IP addresses for internal traffic. A NAT box located where the
LAN meets the Internet provides the necessary IP address translation. This helps
provide a sort of firewall and allows for a wider address range to be used
internally without danger of conflict. Using the router’s NAT capability, you can
access the Internet from any computer on your home network without having to
purchase more IP addresses from your ISP.
Port
Network clients (LAN PC) uses port numbers to distinguish one network
application/protocol from another. Below is a list of common applications and
protocol/port numbers.
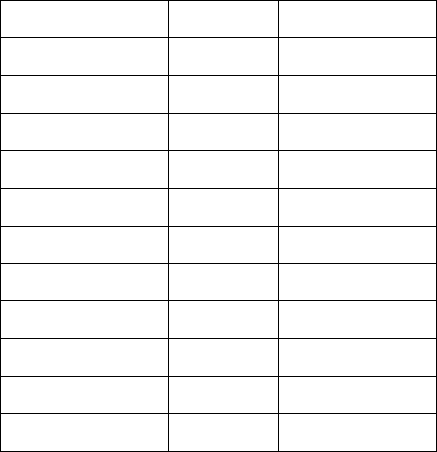
Application
Protocol
Port Number
Telnet
TCP
23
FTP
TCP
21
SMTP
TCP
25
POP3
TCP
110
H.323
TCP
1720
SNMP
UCP
161
SNMP Trap
UDP
162
HTTP
TCP
80
PPTP
TCP
1723
PC Anywhere
TCP
5631
PC Anywhere
UDP
5632


















