59
B
B
:
:
B
B
i
i
n
n
a
a
r
r
y
y
t
t
o
o
H
H
e
e
x
x
a
a
d
d
e
e
c
c
i
i
m
m
a
a
l
l
C
C
o
o
n
n
v
v
e
e
r
r
s
s
i
i
o
o
n
n
s
s
Many of the unit’s configuration procedures require you to assemble a series of
options (represented as bits) into a complete command (represented as a byte). The
resulting binary value must be converted to a hexadecimal representation.
Use this chapter to learn how to convert binary values to hexadecimals or to look up
values in the tables of configuration options in hexadecimal notation. The tables
include:
Connect Mode Options
Disconnect Mode Options
Flush Mode (Buffer Flushing) Options
Interface Mode Options
Pack Control Options
Converting Binary to Hexadecimal
Following are two simple ways to convert binary numbers to hexadecimals.
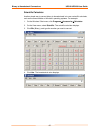
Conversion Table
Hexadecimal digits have values ranging from 0 to F, which are represented as 0-9, A
(for 10), B (for 11), etc. To convert a binary value (for example, 0100 1100) to a
hexadecimal representation, the upper and lower four bits are treated separately,
resulting in a two-digit hexadecimal number (in this case, 4C). Use the following table
to convert values from binary to hexadecimal.
Decimal Binary Hex
0 0000 0
1 0001 1
2 0010 2
3 0011 3
4 0100 4
5 0101 5
6 0110 6
7 0111 7
8 1000 8
9 1001 9
10 1010 A
11 1011 B
12 1100 C
13 1101 D
14 1110 E
15 1111 F