45
Chapter 5: Configuring the Switch through the Web Utility
QoS
24-Port 10/100 + 2-Port Gigabit Switch with Webview and Power over Ethernet
Queue Settings
This switch prioritizes each packet based on the required level of service, using four priority queues with strict or
Weighted Round Robin Queuing. It uses IEEE 802.1p and 802.1Q tags to prioritize incoming traffic based on input
from the end-station application. These functions can be used to provide independent priorities for delay-
sensitive data and best-effort data.
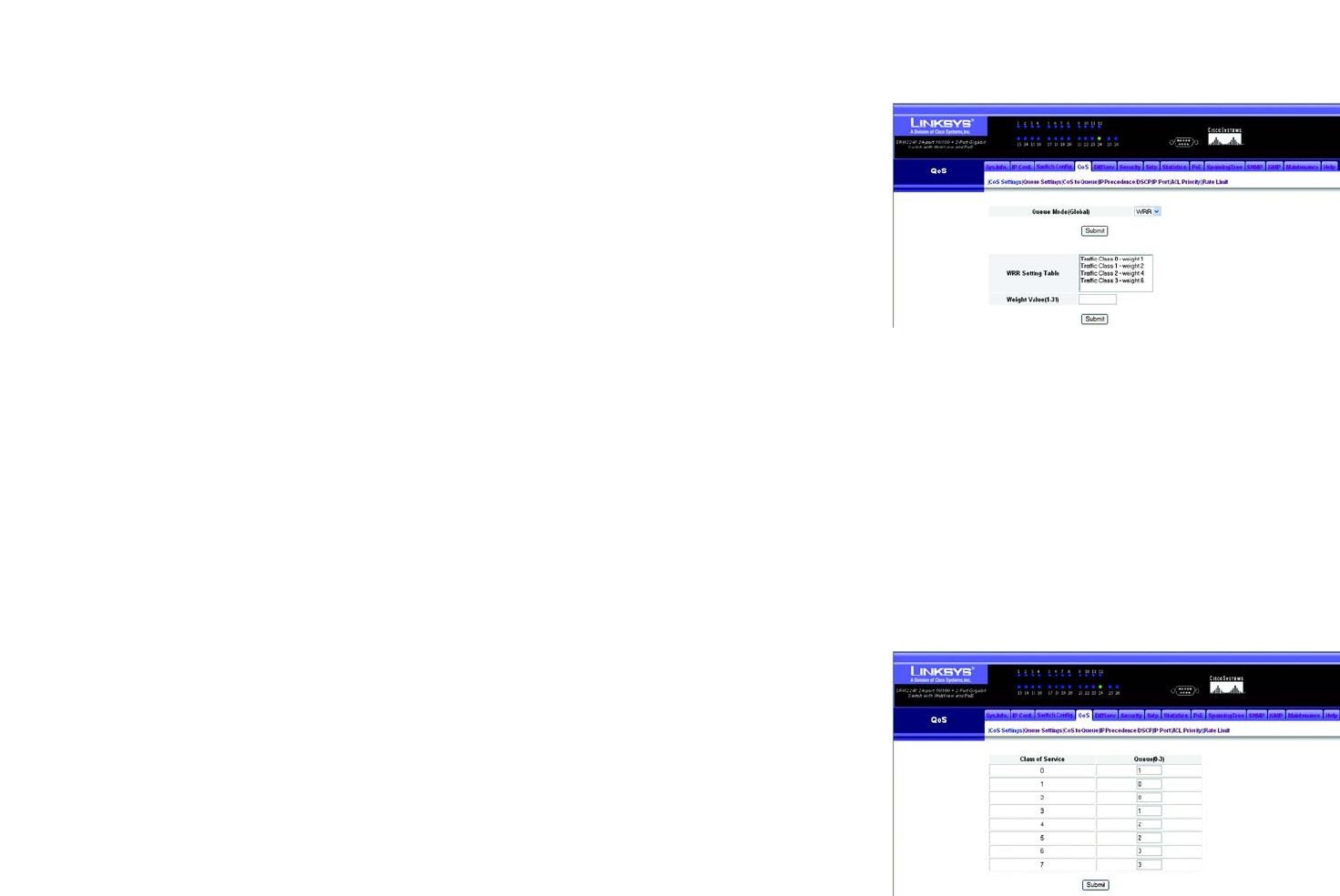
Queue Mode (Global). You can set the switch to service the queues based on a strict rule that requires all traffic
in a higher priority queue to be processed before lower priority queues are serviced, or use Weighted Round-
Robin (WRR) queuing that specifies a relative weight of each queue. WRR uses a predefined relative weight for
each queue that determines the percentage of service time the switch services each queue before moving on to
the next queue. This prevents the head-of-line blocking that can occur with strict priority queuing.
• WRR. Weighted Round-Robin shares bandwidth at the egress ports by using scheduling weights 1, 2, 4, 6
for queues 0 through 3 respectively.
• Strict. Services the egress queues in sequential order, transmitting all traffic in the higher priority queues
before servicing lower priority queues.
Set the Queue Mode to Strict or WRR using the Queue Mode drop-down menu then click submit.
Enter a weight, select a traffic class (that is, output queue) then click submit to save the changes.
Weight Value. Set a new weight for the selected traffic class. However, note that Queue 0 is fixed at a weight of
1, and cannot be configured. (Range: 1-31)
CoS to Queue
Class of Service. CoS value. (Range: 0-7, where 7 is the highest priority)
Queue. Output queue buffer. (Range: 0-3, where 3 is the highest CoS priority queue)
Assign priorities to the traffic classes (that is, output queues) for the selected interface.
Click submit to save the changes.
Figure 5-26: QoS - Queue Settings
Figure 5-27: QoS - CoS to Queue


















