General Description
MN102H Series Description
MN102H75K/F75K/85K/F85K LSI User Manual Panasonic Semiconductor Development Company
25
Panasonic
■ Interrupt controller
An interrupt controller external to the core controls all nonmaskable and
maskable interrupts except reset. There are a maximum of sixteen interrupt
classes (class 0 to 15). Each class can have up to four interrupt factors and any of
seven priority levels.
The CPU checks the processor status word to determine whether or not to accept
an interrupt request. If it accepts the request, automatic hardware servicing
begins and the contents of the program counter and other necessary registers are
pushed to the stack. The program then looks up and branches to the entry address
of the interrupt service routine for the interrupt that occurred.
Note: Interrupt control hardware configuration varies between products.
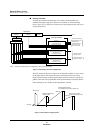
Figure 1-6 Interrupt Controller Configuration
0123456
Interrupt Masking
Nonmaskable Interrupt
Receive
Reset
Receive
Interrupt Enable
Maskable Interrupt
Receive
Reset
CPU Core
4
Group 4
Maskable Interrupt Controllers
Maskable Interrupt
Control Registers (xx ICR)
4
External NMI pin input
Watchdog timer
Undefined instruction
Interrupt occurred,
but no vector exists
Maskable interrupts
Max. 240 vectors
External pin interrupts
Peripheral interupts
Group 63
Maskable Interrupt Controllers
Maskable Interrupt
Control Registers (xx ICR)
Interrupt Controller
4
Groups 0-3
Nonmaskable Interrupt Controllers
Nonmaskable Interrupt
Control Registers (NMICR)
(
Nonmaskable interrupts
)
()
(WDICR)
(UNICR)
(EIICR)
Figure 1-7 Interrupt Servicing Sequence
Hardware processing
Push PC, PSW
Interrupt
Main program
x'080008'
Interrupt service routine
Header resets interrupt vector
Interrupt preprocessing
Push registers, branch to entry address, etc.
JMP, etc.
Max. 6 machine cycles
7 machine cycles