12-2 Administration Guide
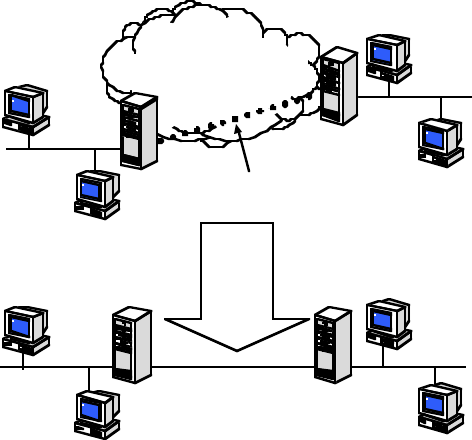
Tunneling is a process of creating a private path between a remote user or private network and another private
network over some intermediate network, such as the IP-based Internet. A VPN allows remote offices or
employees access to your internal business LAN through means of encryption allowing the use of the public
Internet to look “virtually” like a private secure network. When two networks communicate with each other
through a network based on the Internet Protocol, they are said to be tunneling through the IP network.
Unlike the phone company, private and public computer networks can use more than one protocol to carry your
information over the wires. Three such protocols are in common use for tunnelling, Point-to-Point Tunnelling
Protocol (PPTP), Ascend Tunnel Management Protocol (ATMP), and IP Security (IPsec). The Netopia Router can
use any one.
■ Point-to-Point Tunneling Protocol (PPTP) is an extension of Point-to-Point Protocol (PPP) and uses a client
and server model. Netopia’s PPTP implementation is compatible with Microsoft’s and can function as
either the client (PAC) or the server (PNS). As a client, a Netopia R-series router can provide all users on a
LAN with secure access over the Internet to the resources of another LAN by setting up a tunnel with a
Windows NT server running Remote Access Services (RAS) or with another Netopia Router. As a server, a
Netopia R-series router can provide remote users a secure connection to the resources of the LAN over a
dial-up, cable, DSL, or any other type of Internet access. Because PPTP can create a VPN tunnel using the
Dial-Up Networking (DUN) (see Dial-Up Networking for VPN on page 12-15) utility built into Windows 95, 98,
or NT, no additional client software is required.
■ Ascend Tunnel Management Protocol (ATMP) is the protocol that is implemented in many Ascend routers.
ATMP is a simple protocol for connecting nodes and/or networks together over the Internet via a tunnel.
ATMP encapsulates IP or other user data without PPP headers within General Routing Encapsulation (GRE)
protocol over IP. ATMP is more efficient than PPTP for network-to-network tunnels.
■ IPsec stands for IP Security, a set of protocols that supports secure exchange of IP packets at the IP layer.
IPsec is deployed widely to implement Virtual Private Networks (VPNs). IPsec supports two encryption
modes: Transport and Tunnel. Transport mode encrypts only the data portion (payload) of each packet, but
leaves the header untouched. The more secure Tunnel mode encrypts both the header and the payload. On
Transit Internetwork
Logical
Equivalent
Virtual Private Network


















