104
Overview Section 6-1
6-1 Overview
6-1-1 Socket Service Functions
The socket services allow devices on the Ethernet to send and receive vari-
ous data using the UDP or TCP protocol. The socket services can be used by
CS/CJ-series PCs through the user program by manipulating dedicated bits
(called Socket Service Request Switches) or by executing the CMND(490)
instruction.
The two methods of using the socket services are as follows:
• Dedicated Bits (Socket Service Request Switches)
Requests can be made to a socket service by setting parameters and
then merely manipulating specific Socket Service Request Switches.
• CMND(490)
Requests can be made to a socket service by sending service request
commands to the Ethernet Unit.
Note One of the main differences between using Socket Service Request Switches
and using CMND(490) is in the number of sockets that can be connected
simultaneously, as shown in the following table.
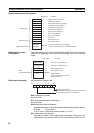
Using Socket Service Request Switches
Note 1. Socket Service Request Switches in the CPU Bus Area in the CIO Area
are used to send a service request from the CPU Unit to the Ethernet Unit.
2. The Socket Service Parameters in the CPU Bus Unit Area in the DM Area
are used to specify the service being requested from the Ethernet Unit.
The CPU Bus Unit Area in the DM Area is also used to receive results of
processing from the Ethernet Unit to the CPU Unit.
Using CMND(490)
Protocol Socket Service Request
Switches
CMND(490)
UDP Total of 8 sockets max. 8 sockets max.
TCP 8 sockets max.
CS/CJ-series PC
CPU Unit
Ethernet Unit
Socket Service
Request Switches
Socket Service
Parameters
Refreshed
(See note 1.)
Refreshed
(See note 2.)
TCP data
transfers
UDP data
transfers
Host computer
or other device
System
call
User program
Sockets
Sockets
CS/CJ-series PC
CPU Unit Ethernet Unit
TCP data
transfers
UDP data
transfers
Host computer or other device
System
call
User program
FINS
command
FINS response
Processing
results
Sockets
Sockets