Using the Web Interface 4-25
Basic Security Configurations
There are two main decisions to be made when choosing wireless security:
encryption method and authentication protocol. The encryption method
determines the algorithm used to encrypt the message. The authentication
type specifies how users are identified and verified on a network. Is the
device seeking connection what (and who) it claims to be?
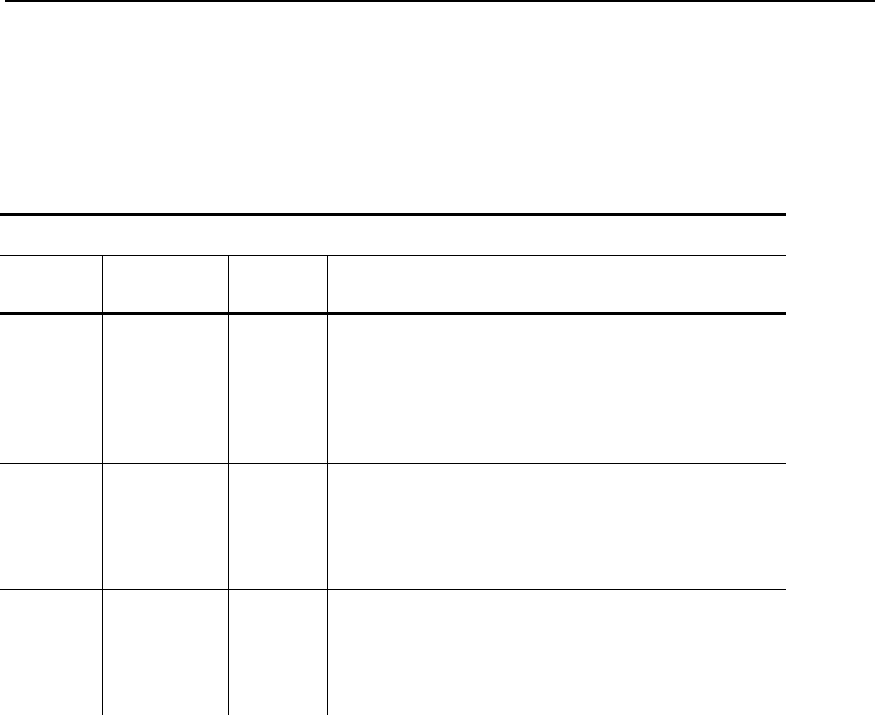
Select an Encryption Method from the following table:
Encryption Method
Type Algorithm
Size
(bits)
Description
WEP RC 4 64/128
This is the 64 or 128 bit WEP Key that
must match other nodes’ encryption keys
in order to communicate. The user can
only define 10 hex characters (40 bits) for
64 bit WEP or 26 characters (104 bits) for
128 bit WEP.
WPA RC 4 64/128
Improves on WEP by using TKIP*
(Temporal Key Integrity Protocol), which
dynamically changes the encryption key
and MIC (Message Integrity Code), which
replaces CRC.
WPA 2 AES 128
Improves on WPA by replacing RC 4 with
AES (Advanced Encryption Standard) for
encryption. The user can only define 26
characters (104 bits) for 128 bit
WPA 2.
* Dynamic WEP cannot be selected directly, so select 128 for the
encryption mode and select an authentication mode from one of the
following: LEAP, PEAP, EAP-FAST, TLS, or TTLS.


















