Version 3.1-en Solaris 10 Container Guide - 3.1 4. Best Practices Effective: 30/11/2009
4.1.7.4. Exclusive IP instance
[dd] With exclusive IP instances, an almost complete separation of the network stacks between zones
is achieved (from Solaris 10 8/07).
A zone with an exclusive IP instance has its own copy of variables and tables that are used by the
TCP/IP stack. As a result, this zone has its own IP routing table, ARP table, IPsec policies, IP filter
rules or ndd settings. Within the zone with an exclusive IP instance, the use of ifconfig(1M)
plumb, snoop(1M), dhcp(5) or ipfilter(5) is possible.
To use exclusive-IP at least one separate physical or tagged VLAN network interface has to be
assigned to a zone and the ip-type attribute has to be set accordingly (zonecfg: set ip-
type). Tagged VLAN interfaces get their own names that are composed as follows:
Interface = Interfacename<Instance + (VLAN-ID * 1000)>
e.g. bge4003 uses the VLAN with ID 4 on bge3
The admin of the local zone himself configures the IP address on the interface. The following
interfaces are currently GLDv3-enabled: bge, e1000g, ixgb, nge, rge, xge. Although the older ce-
interfaces are not GLDv3-enabled, but they are supported as well.
Further details on supported network interface cards can be found at:
http://opensolaris.org/os/project/crossbow/faq/#ip_instances
4.1.7.5. Firewalls between zones (IP filter)
[dd] Firewalls can be used in zones to filter packages or for NAT. Thus, for example, the data traffic
between certain zones can be completely prevented or limited for a network port. If the firewall is to
be used on the system itself together with the zones, two versions can be distinguished in general:
• For shared IP zones: The firewall and its rules must be configured, started and administered in
the global zone.
• For exclusive IP zones: The firewall and its rules must be configured, started and administered
in the respective local zone.
IP filter is part of Solaris 10 and OpenSolaris. It contained as a firewall and was extended such that it
can also be used as a firewall between a system's shared IP zones.
(Cookbook: 5.2.5 IP filter between shared IP zones on a system )
(Cookbook: 5.2.6 IP filter between exclusive IP zones on a system )
42
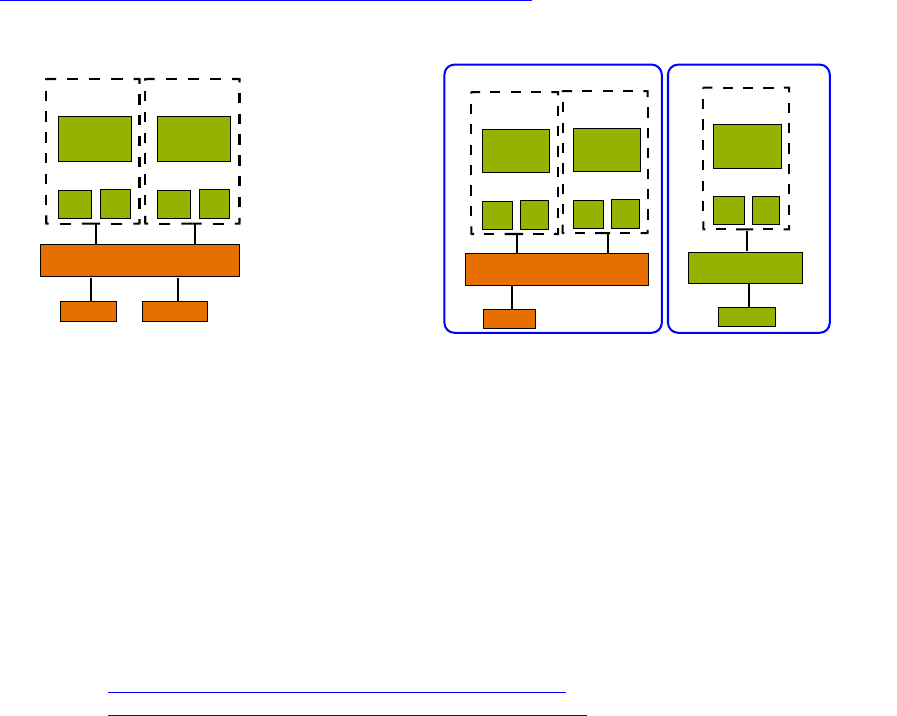
Figure 24: [dd] Comparison between shared IP instance (left) and exclusive IP instance (right)
IP/ARP/IPsec
bge1000ce0
tcp
udp
apps
Global Zone
tcp
udp
apps
Zone A
129.146.89.2 129.146.89.3
IP/ARP/IPsec
bge1000
ce0
tcp
udp
apps
Global Zone
shared IP
tcp
udp
apps
Zone “bar”
shared IP
129.146.89.2 129.146.89.3
tcp
udp
apps
Zone “foo”
exclusive IP
IP/ARP/IPsec
10.0.0.1
Instance #0 Instance #1


















