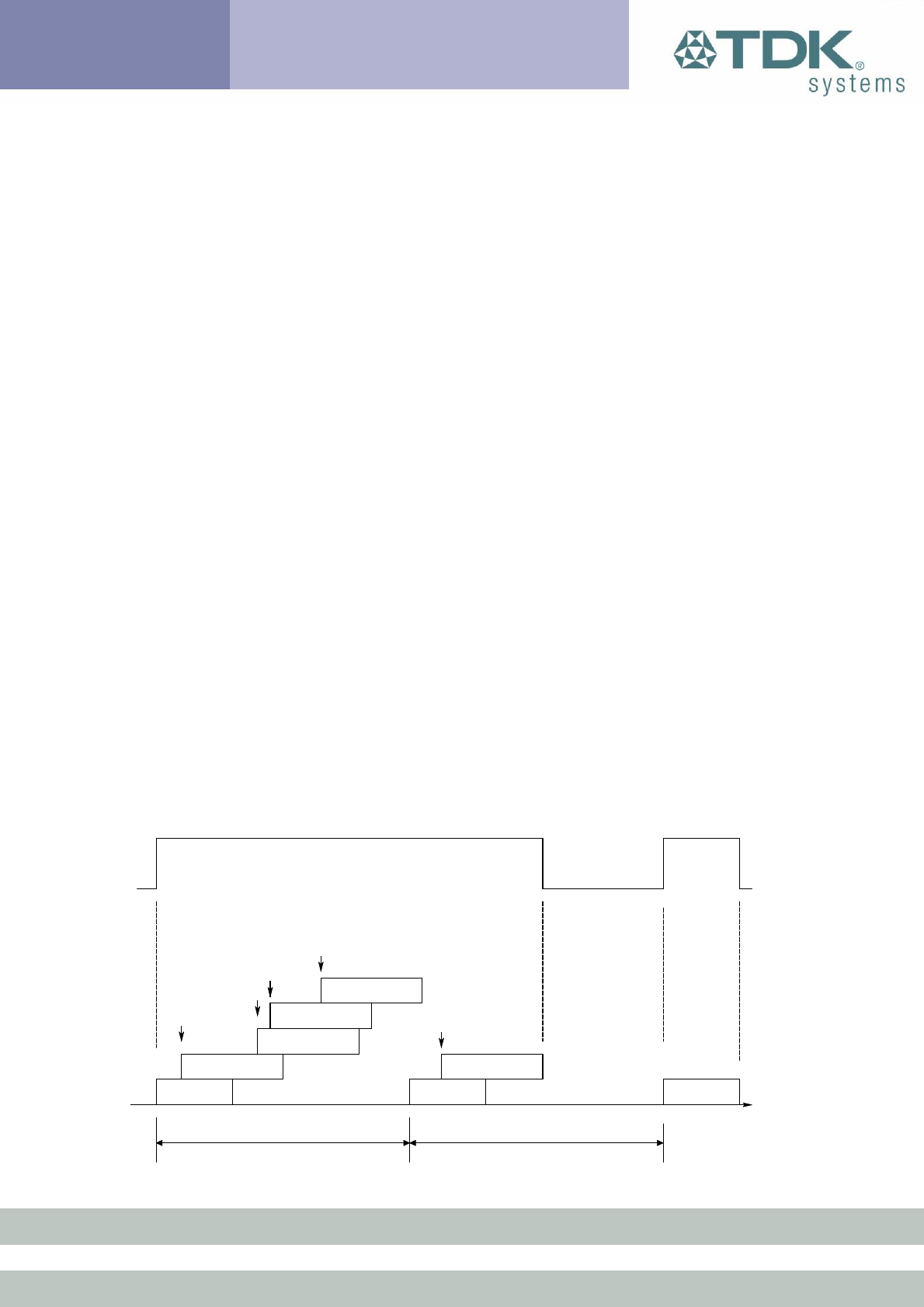
contacted during N-M slots, and so can switch its power hungry circuitry
off. The specification goes further by also specifying a third parameter
called ‘timeout’ (T) which specifies ‘extra’ timeslots that the slave will
agree to listen for after receiving a valid data packet. Put another way, if
a data packet is received by the slave, then it knows that it MUST carry
on listening for at least T more slots. If within that T slot time period
another data packet is received, then the timer is restarted. This
mechanism ensures low power consumption when there is no data
transfer – at the expense of latency. When there is a lot of data to be
transferred, it acts as if sniff mode were not enabled.
It is stated above that during sniff mode, a slave listens for N slots every
M slots. The Bluetooth specification states that a master can have up to
7 slaves attached to it with all slaves having requested varying sniff
parameters. It may therefore be impossible to guarantee that each slave
gets the M parameter it requested. In light of this, the protocol for
enabling sniff mode specifies that a requesting peer specify the M
parameter as a minimum and maximum value. This will allow the master
to interleave the sniff modes for all slaves attached.
For this reason, the sniff parameters are specified in TDK module via
four S registers. S Register 561 is used to specify ‘N’, S Register 562 is
used to specify ‘T’ and S Registers 563/564 are used to specify
minimum ‘M’ and maximum ‘M’ respectively. Although the specification
defines these parameters in terms of timeslots, the S register values
have to be specified in units of milliseconds and the firmware does the
necessary translation to timeslots.
Data Exhange
High Power Consumption
Low Power Consumption
M
Slots (Negotiated)
M
Slots (Negotiated)
N
Slots
N
Slots
N
Slots
T
Slots
T
Slots
T
Slots
T
Slots
T
Slots
Data Exchange
Data Exchange
Data Exchange
Data Exchange
Data Exchange
20 of 36