GLOSSARIES ENGLISH VERSION EO1-33087
GLOSSARIES
GLOSSARIES
Bar code
A code which represents alphanumeric characters
by using a series of black and white stripes in
different widths. Bar codes are used in various
industrial fields: Manufacturing, Hospitals,
Libraries, Retail, Transportation, Warehousing, etc.
Reading bar codes is a fast and accurate means of
capturing data while keyboard entry tends to be
slow and inaccurate.
Batch mode
Issue mode that continuously prints media until the
required number has been printed.
Black mark
A mark printed on the media enabling the printer to
detect the correct start position of the media,
helping to maintain constant print position.
Black mark sensor
A reflective sensor that detects the difference
between a black mark and the print area to find the
print start position.
Cut mode
Printer mode of operation where an (optional)
cutter module is installed to automatically cut
media from the supply roll after they are printed.
The print command can specify to cut every media
or to cut after a set number of media have been
printed.
Direct thermal printing
A printing method using no ribbon, but thermal
media which reacts to heat. The thermal print head
heats the thermal media directly, causing print
image to be printed on the media.
DPI
Dots Per Inch
A unit used to express print density or resolution.
Feed gap sensor
A transmissive sensor that detects the difference
between the gap between labels and the label itself,
to find the print start position of the label.
Font
A complete set of alphanumeric characters in one
style of type. E.g. Helvetica, Courier, Times
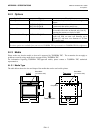
Gap
Distance from the bottom of one label to the top of
the next label.
IPS
Inch per second
A unit used to express print speed.
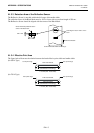
Label
A type of media with adhesive backing supplied on
a backing paper.
Media
Material on which images are printed by the printer.
Label, tag paper, fanfold paper, perforated paper,
etc.
Printer driver
A software program that will convert the
application program’s printing request into the
language that the printer understands.
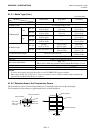
Print head element
The thermal print head consists of a single line of
tiny resistive elements which when current is
allowed to flow through them it heats up causing a
small dot to be burned onto thermal paper or a
small dot of ink to be transferred from a thermal
ribbon to ordinary paper.
Printing speed
The speed at which printing occurs. This speed is
expressed in units of IPS (inches per second).
Resolution
The degree of detail to which an image can be
duplicated. The minimum unit of divided image is
called a pixel. As the resolution becomes higher,
the number of pixels increases, resulting in a more
detailed image.
Ribbon
An inked film used to transfer an image onto the
media. In the thermal transfer printing, it is heated
by the thermal print head, causing an image to be
transferred onto the media.
Strip mode
One of the printer modes of operation where an
optional strip module is installed to separate
printed labels from the backing paper one by one.