Access Control Lists
3-75
3
and compared with the address for each IP packet entering the port(s) to which this
ACL has been assigned.
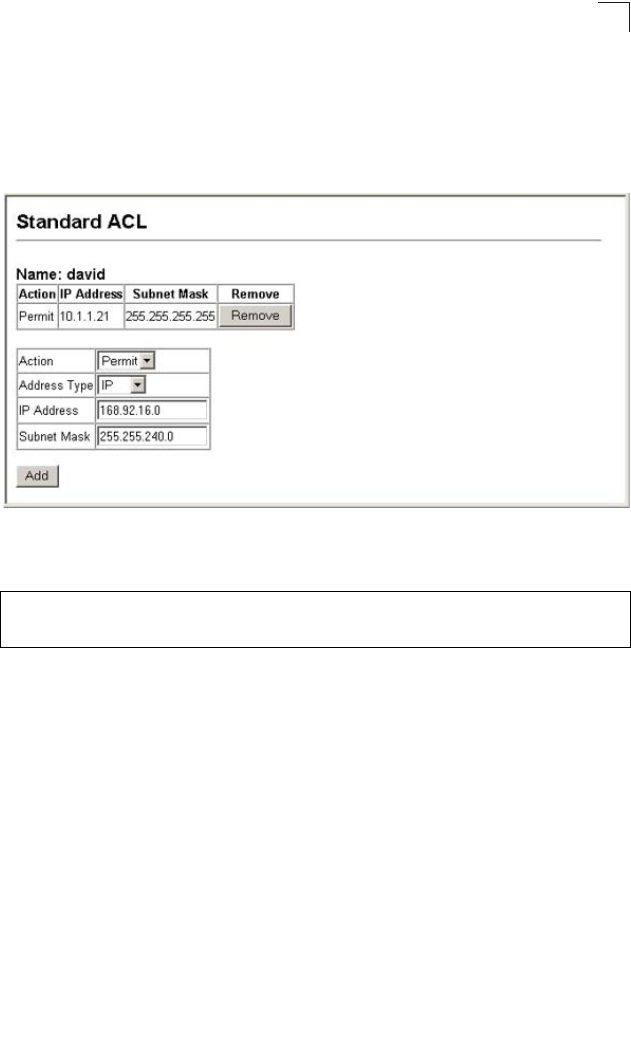
Web – Specify the action (i.e., Permit or Deny). Select the address type (Any, Host,
or IP). If you select “Host,” enter a specific address. If you select “IP,” enter a subnet
address and the mask for an address range. Then click Add.
Figure 3-45 ACL Configuration - Standard IP
CLI – This example configures one permit rule for the specific address 10.1.1.21
and another rule for the address range 168.92.16.x – 168.92.31.x using a bitmask.
Configuring an Extended IP ACL
Command Attributes
• Action – An ACL can contain any combination of permit or deny rules.
• Source/Destination Address Type – Specifies the source or destination IP
address. Use “Any” to include all possible addresses, “Host” to specify a specific
host address in the Address field, or “IP” to specify a range of addresses with the
Address and SubMask fields. (Options: Any, Host, IP; Default: Any)
• Source/Destination IP Address – Source or destination IP address.
• Source/Destination Subnet Mask – Subnet mask for source or destination
address. (See the description for SubMask on page 3-74.)
• Service Type – Packet priority settings based on the following criteria:
- Precedence – IP precedence level. (Range: 0-7)
- TOS – Type of Service level. (Range: 0-15)
- DSCP – DSCP priority level. (Range: 0-63)
Console(config-std-acl)#permit host 10.1.1.21 4-89
Console(config-std-acl)#permit 168.92.16.0 255.255.240.0
Console(config-std-acl)#


















