Remote Operation 77
If you want to disable this facility, send the command.
PON 0
If you want to find out if the power-on SRQ is enabled or disabled, send the following query:
PON ?
and address the supply to talk. The supply will respond with a 1 or 0 as discussed above.
NOTE The power-on (PON) SRQ mode is stored in the non-volatile memory of the supply so that although the
supply may be switched off, it will remember the status of the last PON command at power-on and
respond accordingly.
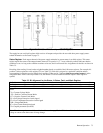
Table 5-7 summarizes all the conditions under which a service request will be generated.
Table 5-7 Condition for Generating a Service Request
Condition Commands Sent State of
PON SRQ RQS Bit
•
Any
0 0 0
•
Power-on
1 - 1
•
Error
- 2 or 3 1
•
Fault
-1 or 3 1
Reprogramming Delay
The power supply may switch modes or become unregulated momentarily after a new output value is programmed.
Because of their short duration, these cases may not ordinarily be considered a fault but the supply will recognize this
deviation and generate a fault signal. To prevent this, the reprogramming delay feature is implemented.
Reprogramming delay will delay the onset of certain fault conditions and prevent the power supply from registering a fault
when these conditions are true. When the delay is in effect, the CV, + CC, - CC and UNR bits of the status register are
masked and cannot communicate with the mask and fault registers and the OCP function. This will prevent the supply from
registering a fault should any of these bits become set during the delay period. Reprogramming delay is initiated when any
of the following functions are executed:
VSET: ISET: RCL: OVRST: OCRST; OUT on/off
At power-on reprogramming delay is set to 20 mS. You can specify new values between 0 and 32 S in steps of 4 mS. If you
specify a value which is not a multiple of 4 mS, the supply will round off the set value to the nearest 4 mS multiple.
To program a new value of 80 mS in output 2 for example, send the following:
DLY 2,.08
If you send a value outside the 0 to 32 S range you will get a programming error. You may use the programming response
times in the specifications table to give you an idea of a typical delay setting. However, the appropriate delay setting will
also depend on load capacitance, load resistance, and current limit setting. See page 51 for output capacitor considerations.
To query the reprogramming delay setting of a particular output channel, send the following query:
DLY? 2 (using output 2 as an example)