Chapter 11 Avaya P330 Layer 2 Features
70 Avaya P332GT-ML User’s Guide
LAG
LAG Overview
A LAG uses multiple ports to create a high bandwidth connection with another
device. For example: Assigning four 100BASE-T ports to a LAG on an Avaya P330
allows the switch to communicate at an effective rate of 400 Mbps with another
switch.
LAGs provide a cost-effective method for creating a high bandwidth connection.
LAGs also provide built-in redundancy for the ports that belong to a LAG. If a port
in a LAG fails, its traffic is directed to another port within the LAG.
The behavior of the LAG is derived from the base port (the first port that becomes a
LAG member). The attributes of the base port, such as port speed, VLAN number,
etc., are applied to all the other member ports in the LAG.
When created, each LAG is automatically assigned a logical port number (usually
designated 10x). This logical port number can then be used as any regular panel
port for all configuration required for the LAG (Spanning Tree, Redundancy, etc.)
Note: In the P330-ML switches you need to erase all ports in t.he LAG in order to
remove it.
LAG CLI Commands
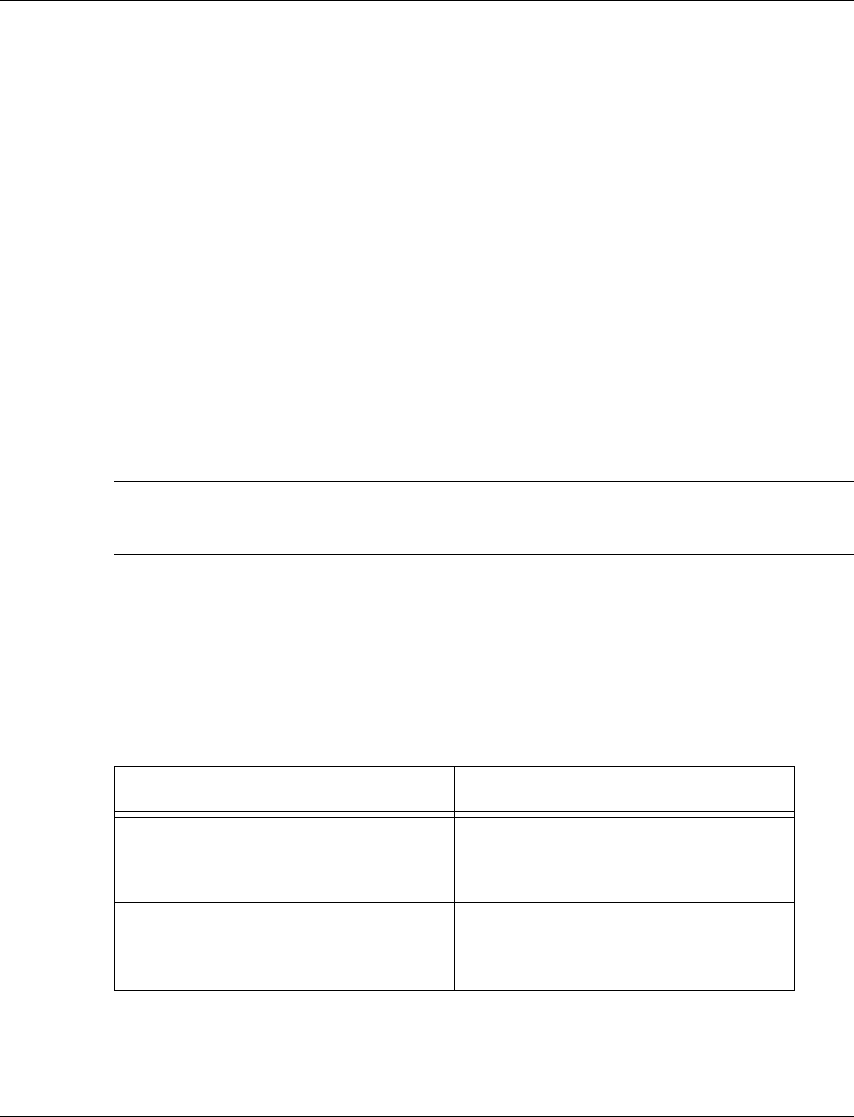
The following table contains a list of the CLI commands for the LAG feature. The
rules of syntax and output examples are all set out in detail in the P330 Reference
Guide.
Table 11.5 LAG CLI Commands
In order to... Use the following command...
Enable or disable a Link
Aggregation Group (LAG) logical
port on the switch
set port channel
Display Link Aggregation Group
(LAG) information for a specific
switch or port
show port channel