89
APPENDIX
Progressive
An image display system used to display the entire screen per scan. When an interlace
signal (video signal) that displays one screen by two scans (one for odd lines and one for
even lines) is input, progressive processing is required. When the progressive function is
turned off, one screen is displayed using image signals per interlace signal, deteriorating the
vertical resolution of the image. When the progressive function is turned on, one screen is
displayed using image signals per two interlace signals, improving the vertical resolution of
the image. Turn off the progressive function when flickering and horizontal lines are
noticeable on a fast-moving picture.
Resolution
The number of dots (horizontal dots x vertical dots) that can be displayed on a computer is
called “resolution of display”. Resolution indicates the size of the display area (amount of
information).
Selecting SXGA+ (1400 dots x 1050 dots) as the display resolution of the computer allows
this projector to project high-resolution images. If your computer does not have the SXGA+
option, select the maximum resolution among the selectable options.
Gamma Correction
A tone adjustment system used during projection of image data. The gamma correction
function works effectively when portions of an image are obscure because they are too light
or dark.
This projector supports manual gamma correction, automatic gamma correction, and
dynamic gamma correction.
DVI-I
A digital video signal connection interface. This interface allows digital data to be sent and
received without conversion to analog data, assuring high image quality with no signal
degradation. The DVI-I (integrated) connector can be used to send and receive analog RGB
video signals in addition to digital signals.
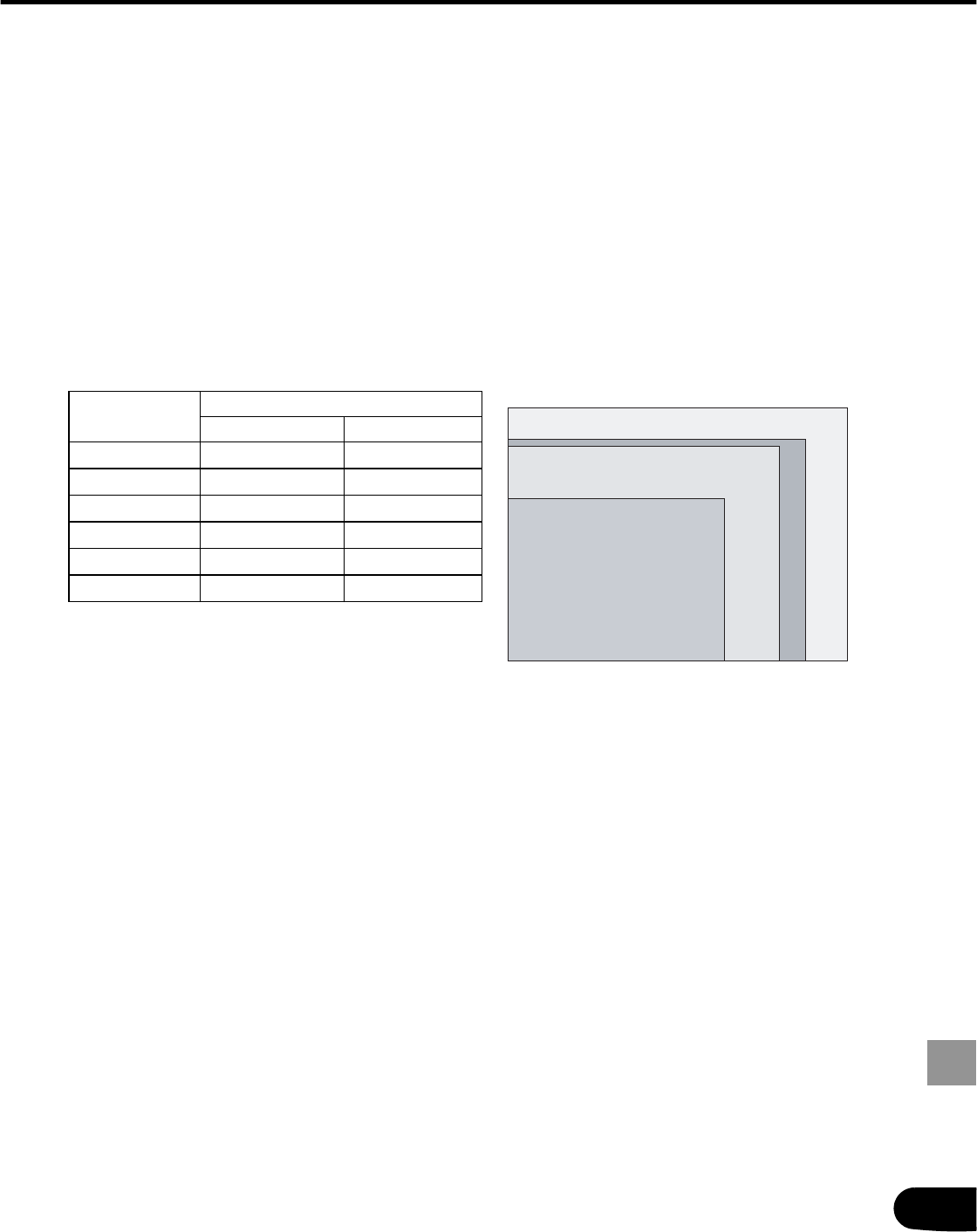
Resolution
Number of dots
Horizontal Vertical
VGA 640 480
SVGA 800 600
XGA 1024 768
SXGA 1280 1024
SXGA+ 1400 1050
UXGA 1600 1200
XGA 1024 x 768 (4:3)
SXGA 1280 x 1024 (5:4)
SXGA + 1400 x 1050 (4:3)
UXGA 1600 x 1200 (4:3)
Number of pixels in each resolution