72-36
Cisco ASA 5500 Series Configuration Guide using ASDM
Chapter 72 Configuring Clientless SSL VPN
Understanding How KCD Works
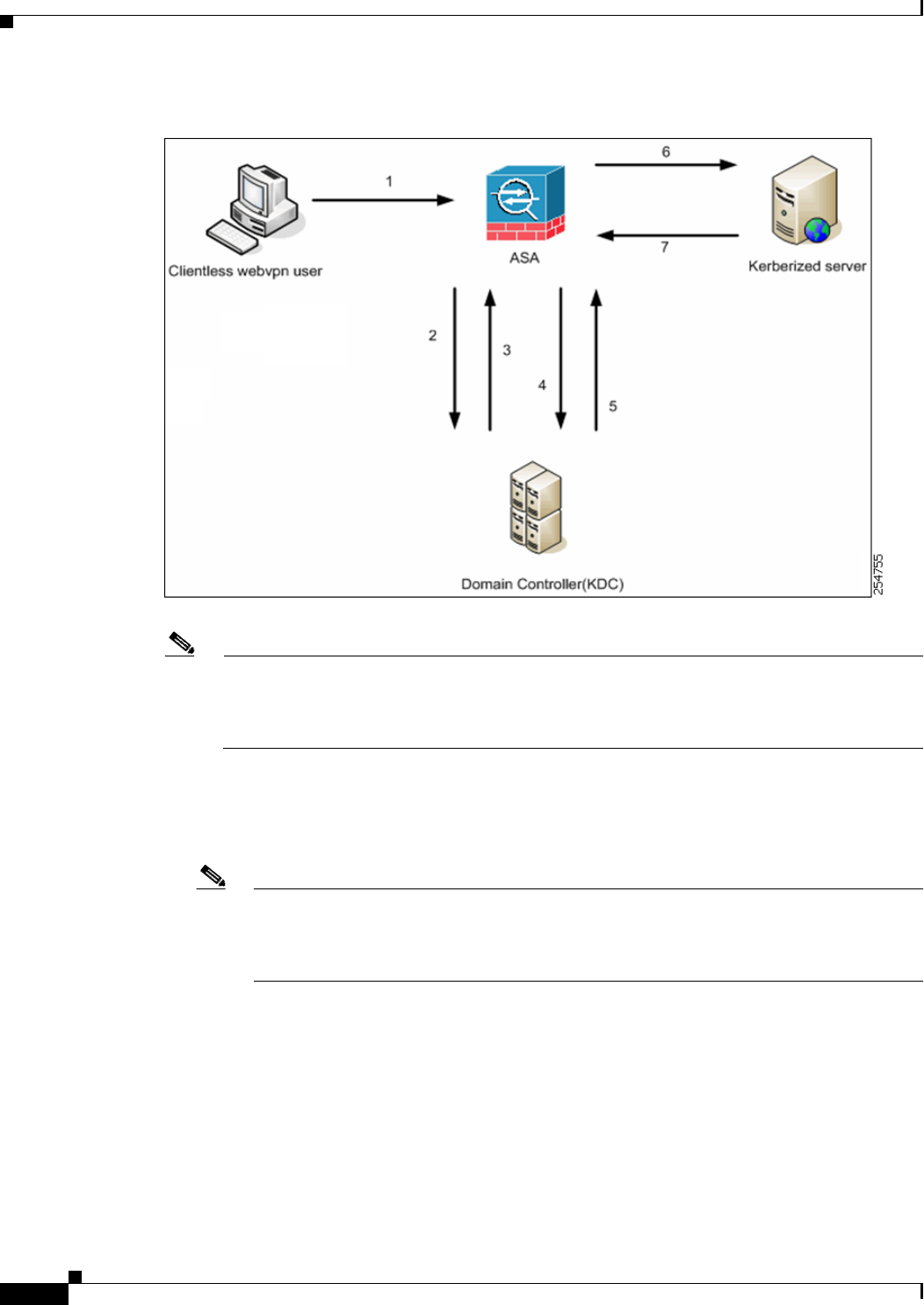
Figure 72-7 KCD Process
Note A clientless user session is authenticated by the ASA using the authentication mechanism
configured for the user. (In the case of Smartcard credentials, ASA performs LDAP
authorization with the userPrincipalName from the digital certificate against the Windows
Active Directory).
1. After successful authentication, the user logs in to the ASA clientless portal page. The user accesses
a Web service by entering a URL in the portal page or by clicking on the bookmark. If the Web
service requires authentication, the server challenges ASA for credentials and sends a list of
authentication methods supported by the server.
Note KCD for Clientless SSL VPN is supported for all authentication methods (RADIUS,
RSA/SDI, LDAP, digital certificates, and so on). Refer to the AAA Support table at
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/partner/docs/security/asa/asa84/configuration/guide/access_a
aa.html#wp1069492.
2. Based on the HTTP headers in the challenge, ASA determines whether the server requires Kerberos
authentication. (This is part of the SPNEGO mechanism.) If connecting to a backend server requires
Kerberos authentication, the ASA requests a service ticket for itself on behalf of the user from the
key distribution center.
3. The key distribution center returns the requested tickets to the ASA. Even though these tickets are
passed to the ASA, they contain the user’s authorization data.ASA requests a service ticket from the
KDC for the specific service that the user wants to access.


















