730 Spanning Tree Commands
port. In this way, the root guard enforces the position of the root bridge. In
MSTP scenario the port may be designated in one of the instances while
being alternate in the CIST, and so on. Root guard is a per port (not a per port
per instance command) configuration so all the MSTP instances this port
participates in should not be in root role.
STP BPDU Filtering - STP BPDU filtering applies to all operational edge
ports. Edge Port in an operational state is supposed to be connected to hosts
that typically drop BPDUs. If an operational edge port receives a BPDU, it
immediately loses its operational status. In that case, if BPDU filtering is
enabled on this port then it drops the BPDUs received on this port.
STP BPDU Flooding - STP BPDU flooding feature applies to the STP
disabled switch. To enable BPDU flooding on a port, STP should be disabled
on the switch administratively. When this feature is enabled on the switch, it
floods all the ports with the BPDU flood feature enabled on it.
Commands in this Chapter
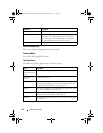
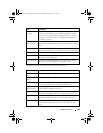
This chapter explains the following commands:
clear spanning-tree
detected-protocols
spanning-tree
auto-portfast
spanning-tree max-
age
spanning-tree portfast
bpdufilter default
exit (mst) spanning-tree bpdu
flooding
spanning-tree max-
hops
spanning-tree portfast
default
instance (mst) spanning-tree
bpdu-protection
spanning-tree
mode
spanning-tree port-
priority
name (mst) spanning-tree cost spanning-tree mst
configuration
spanning-tree priority
revision (mst) spanning-tree
disable
spanning-tree mst
cost
spanning-tree tcnguard
show spanning-tree spanning-tree
forward-time
spanning-tree mst
port-priority
spanning-tree transmit
hold-count
show spanning-tree
summary
spanning-tree
guard
spanning-tree mst
priority
spanning-tree spanning-tree
loopguard
spanning-tree
portfast
2CSPC4.XCT-SWUM2XX1.book Page 730 Monday, October 3, 2011 11:05 AM