13
Chapter 2. Getting Started the BHT and System Mode
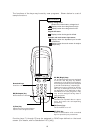
■ Host Computer
Models: PC/AT, PS/2
Optional application programs and OSes
BHT-BASIC3.5
MS-DOS Win3.1 Win95 Win98 WinNT3.5/4.0
Win2000
Professional
BHT-BASIC Compiler
BHT-BASIC3.0
(MS-DOS–based)
BHT-BASIC3.0
(Windows3.1-
based)
OS
Applications
Ir-Transfer Utility C
Ir-Transfer Utility E
Transfer Utility
MS-DOS–
based
MS-DOS–
based
Windows3.1–
based
Win95-/NT-based
Win95-/NT-
based*
Win95-/NT-
based*
Win95-/NT-
based
*This application does not activate any built-in port.
—
—
—
Win95-/NT-
based
Win95-/NT-based
■ CU-7000 and RS-232C Interface Cable (option)
The CU-7000 is an IrDA-compliant communications unit which is required when your
host computer is not equipped with an IrDA interface port. The CU-7000 exchanges
data and programs with the BHT optically, and with the host computer via the RS-232C
interface cable.
You may directly connect two BHTs with each other by using a commercially available
metal cable having 3-pole mini stereo plugs (as a direct-connect interface cable). You
also connect the BHT directly with the host computer or with the modem by using the
direct-connect interface cable compatible with the target equipment. (NOTE: The
direct-connect interface port of the BHT is not designed to stand frequent connecting/
disconnecting. You are, therefore, recommended to use the CU-7000 where you
expect to do a lot of connecting and disconnecting of the BHT to/from a host compu-
ter.)
■ BHT-BASIC Compiler (option)
This Compiler compiles a source program written in BHT-BASIC by an editor of the
host computer running the MS-DOS, into the object program (user program) which
can be used in the BHT. The compiled and linked program file is named "XXX.PD3."
(XXX: File name you can set arbitrarily under the MS-DOS rules) You should download
it to the BHT by using Ir-Transfer Utility C/Ir-Transfer Utility E/Transfer Utility.