4
VLAN (Virtual Local Area Network)
A VLAN is a group of end-stations that are not constrained by their physical location and can communicate as if a common broadcast domain, a LAN. The
primary utility of using VLAN is to reduce latency and the need for routers, by using faster switching instead. Other VLAN utilities include:
Security: Security is increased with the reduction of opportunity in eavesdropping on a broadcast network because
data will be switched to only those confidential users within the VLAN.
Cost Reduction: VLANs can be used to create multiple broadcast domains, thus eliminating the need of expensive
routers.
Port-based (or port-group) VLAN is the common method of implementing a VLAN, and is the one supplied in the Switch.
Features and Benefits
(24) 10/100BASE-TX Fast Ethernet ports + (2) 1000BASE-T Gigabit Ethernet ports or (2) SFP(Mini GBIC) for 2
additional copper or fiber Gigabit connections
Auto MDI/MDI-X support on each port
Full-/half- duplex transfer mode for 10/100Mbps Fast Ethernet transmission
Full-duplex transfer mode for Gigabit Ethernet transmission
Wire-speed reception and transmission
Store-and-Forward switching method
Integrated address Look-Up Engine, supports 8K MAC addresses
Supports 256K bytes RAM for data buffering
Extensive front-panel diagnostic LEDs
Broadcast storm protection
IEEE 802.3x flow control for full-duplex
Back pressure flow control for half-duplex
Support Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP)
Supports MIB for:
RFC1213 MIB II.
Private MIB.
Supports port-base VLAN, 802.1Q-based VLAN
Supports Trunking
Supports Port-mirroring
Supports Port-setting for Speed/Disable, Flow control
Easy configuration via Web Browser
Easy setting via Web Management Utility
Standard 19” Rack-mount size
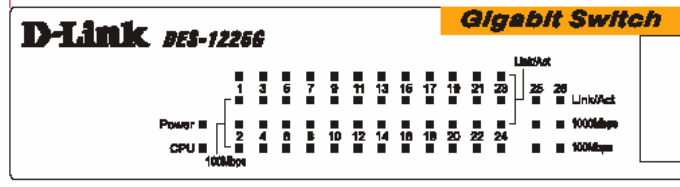
LEDs
LED stands for Light-Emitting Diode.
The front panel LEDs provides instant status feedback and simplifies monitoring and troubleshooting tasks.
Figure 1. LED indicators of the Switch
Power


















