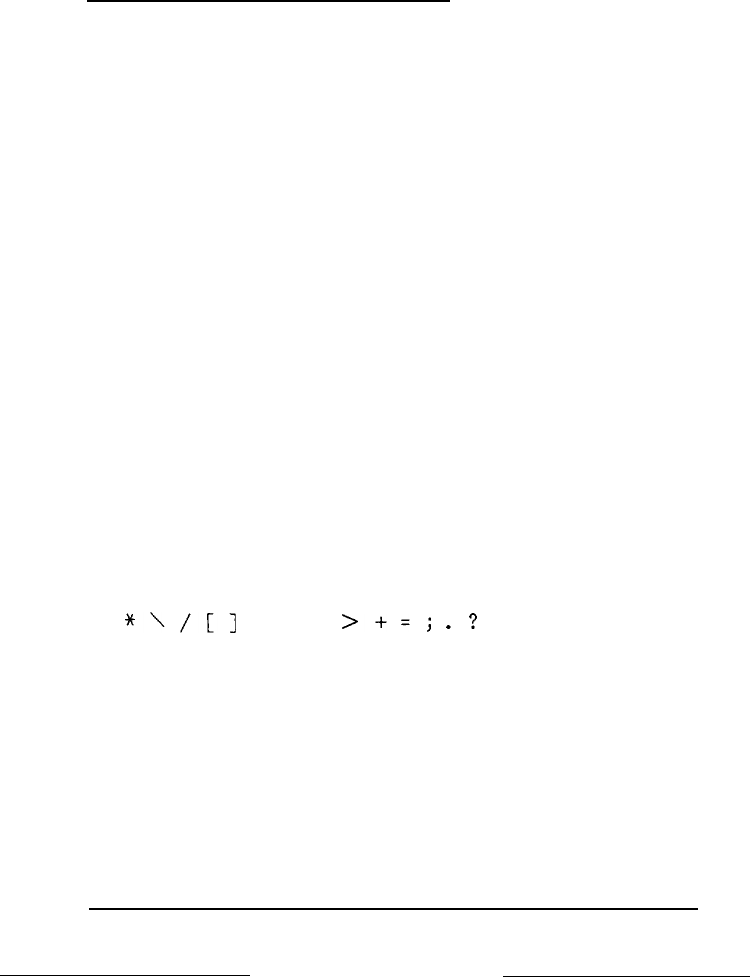
If you press Enter when a command line has an error in it, the
screen displays an error message. Usually, the command prompt
reappears so you can try again. Type the correct command and press
Enter.
Creating and Managing Files
All your data and programs are stored in files. A data file contains
information, such as words, numbers, or pictures. A program file
contains instructions that the computer can understand and execute.
The kind of file you create depends on the MS-DOS command or
application program you use to create it. In general, a data file that
you create using an application program is stored in a special format.
If you use a different application program to read that file, you may
encounter problems.
When you create a file, you need to give it a name. You must name
your files in a certain format required by MS-DOS.
Naming Files
Each file must have a unique filename so you can retrieve it when
you need to. The filename consists of two parts: the name and the
extension.
You can choose a name up to eight characters long. Create a name
that identifies the information the file contains. The name can
contain any characters or numbers except for blank spaces and the
following symbols:
“‘/[I
:I<
>+=;
.?
The extension is optional and can be up to three characters long. You
can use the extension to further identify a file or to describe what
type of file it is, such as a text file or program file. When you use an
extension, separate it from the filename with a period. For example,
an MS-DOS filename might look like this:
DATA.TXT
Using MS-DOS with Your Equity 386
5-5


















