Configuring NAT vs. Transparent mode
FortiGate-30B FortiOS 3.0 MR6 Install Guide
01-30006-0459-20080505 17
Configuring
This section provides an overview of the operating modes of the FortiGate unit,
NAT/Route and Transparent, and how to configure the FortiGate unit for each
mode. There are two ways you can configure the FortiGate unit, using the
web-based manager or the command line interface (CLI). This section will step
through using both methods. Use whichever you are most comfortable with.
This section includes the following topics:
• NAT vs. Transparent mode
• Connecting to the FortiGate unit
• Verify the configuration
• Backing up the configuration
• Additional configuration
NAT vs. Transparent mode
The FortiGate unit can run in two different modes, depending on your network
infrastructure and requirements. You have a choice between NAT/Route mode
and Transparent mode. Both include the same robust network security features
such as antispam, antivirus, VPN and firewall policies.
NAT mode
In NAT/Route mode, the FortiGate unit is visible to the network. Like a router, all
its interfaces are on different subnets.
In NAT mode, each port is on a different subnet, enabling you to have a single IP
address available to the public Internet. The FortiGate unit performs network
address translation before it sends and receives the packet to the destination
network.
In Route mode, there is no address translation.
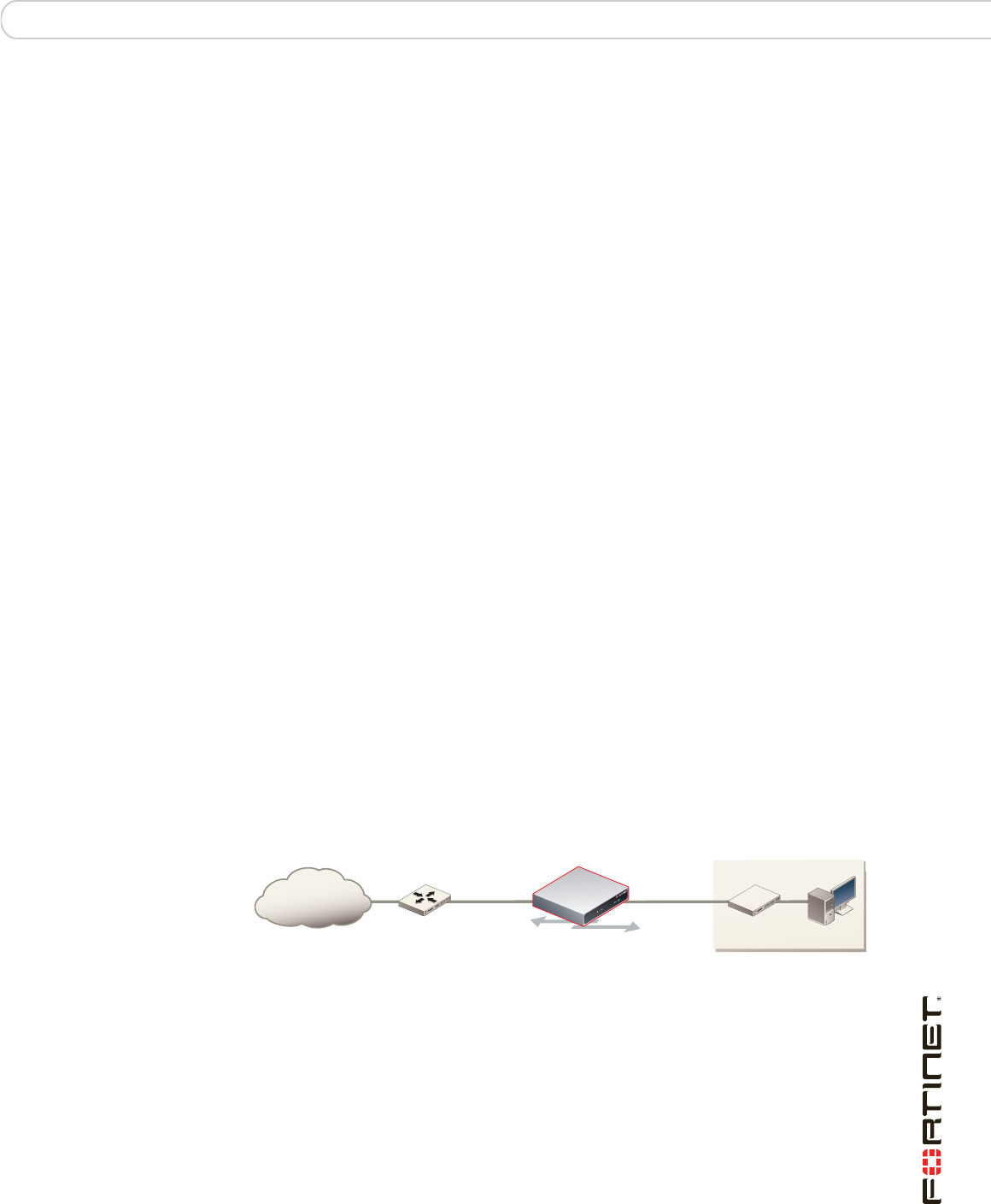
Figure 2: FortiGate unit in NAT mode
You typically use NAT/Route mode when the FortiGate unit is operating as a
gateway between private and public networks. In this configuration, you would
create NAT mode firewall policies to control traffic flowing between the internal,
private network and the external, public network, usually the Internet.
Internet
Router
Internal network
192.168.1.20
192.168.1.99204.23.1.5
NAT mode policies controlling
traffic between internal
and external networks.


















