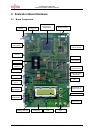
STARTERKIT MB91360
Chapter 4 Details of the included Monitor-Debugger
UG-910006-13 - 18 - © Fujitsu Microelectronics Europe GmbH
DEBUG - STACK: Displays the current stack contents in terms of function calls.
Parameters, if any, are given in brackets.
DEBUG - VECTOR: Reads out and displays the actual interrupt-vector table. Use the „jump“
function to display any code areas pointed to by an interrupt vector (e.g. interrupt service
routines used in your program).
DEBUG - CALL: This function can be used to „call“ any routine defined in your code when
the debugger is halted.
Example: Enter „LCDprinthex(0x1234,4)“ from any example project. The number 1234 will
appear on the LCD. The function-call will be terminated by showing the result (here : none).
You may restore the debugging context by „Clear call“ if execution was stopped during the
function-call. Note that this example assumes that „LCDinitdisp“ was executed before.
DEBUG – LOAD TARGET FILE: Starts a new download of the current load module (ABS
file). Usually this function will be executed automatically after starting the debugger (defined
in debug settings ; see „Project-Setup-Debug“). However, this function can be useful to re-
initialize the debugger for the current debug session.
VIEW - SYMBOL: This function displays all (global) symbols of the current project.
Information about the type (char, integer etc.) and the location (address in RAM or register)
can be shown using „detail“.
VIEW - LOCAL: Similar to View-Symbol, but only local variables of the current function are
shown.
VIEW - COMMAND: From this window, the debugger can be controlled using a command
line input. All GUI functions are available as individual commands.
Examples :
go
step
examine PDRJ
set break main
Dump/Halfword 100000..1000ff
Shortcuts to complex commands can be defined (“alias”) and parameter strings can be
substituted by variables.
Example: candump = Dump/Halfword 100000..1000ff
A set of commands can be combined to a “macro”. Aliases and macros can be defined
using the command window context menu.