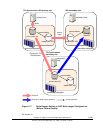
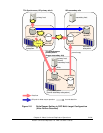
2-34 Chapter 3 Preparing for Universal Replicator z/OS Operations
Hitachi Universal Replicator for IBM /OS User’s Guide
• URz Pair Status
The URz Suspending and Deleting (release) transitional states occur when
a request to change URz pair status has been accepted, but the change to
the requested status (suspended, or simplex) is not yet complete. These
states are not reported to the host. In the case of Suspending, both the
user and the primary storage system can request the status change. In the
case of Deleting (release), only the user can request the status change. If
the user requested the status change, the final status is reported at the
end of the transition. If an error caused the status to change to suspended,
the suspended status is reported at the beginning of the transition.
After a storage system receives a request for splitting or releasing a pair in
Flush mode, the status of the pair will remain Suspending or Deleting
until the journal in the master journal group is restored into the restore
journal group and the pair is completely split or released. To calculate the
time during which the pair remains Suspending or Deleting, use the
following equation:
C × (u ÷ 100) × 1,024 ÷ V (The unit is seconds)
where:
– C is the total capacity of the master journal volume. The unit is
megabytes.
– u is the usage rate of data in the master journal volume. The unit is
percent.
– V is the data transfer speed between the primary and the secondary
storage system. The unit is MB/s (megabytes per second).
To find the usage rate of a journal volume, use the monitoring feature (see
Usage Monitor Window).
The URz SEQCHK status is indicated when a URz pair assigned to a
consistency group with the System timer type accepts a non-time-
stamped update from the primary system. The SEQCHK status does not
affect URz copy activities and will be removed when the next time-stamped
update is successfully copied to the secondary data volume. However, if a
disaster or system failure occurs before the next time-stamped update, the
update sequence consistency between the secondary data volume and
other secondary data volumes in the consistency group is not ensured. To
ensure effective disaster recovery, you should detect and remove the
source of the SEQCHK status. The SEQCHK status can be caused by any of
the following:
– An application may issue update I/Os bypassing the MVS standard I/O
procedure.
– The I/O time-stamping function may not be active at the primary site.
– This URz pair status describes:
• URz suspend types (see the next section),
• URz suspension condition (see section
Suspension Condition).