To see routing changes due to ICMP redirect messages, select NETSTAT menu 2 or
NETSTAT *RTE and then press PF11. Comparing the next hop in this display with
the next hop present in the routing table, you can verify whether a route has been
dynamically changed.
Dead Gateway Processing
RFC-1122, Requirements For Internet Hosts - Communication Layers, requires the IP
layer to include a dead gateway algorithm to manage suspected gateway failures.
This section is intended to give you an overview of dead gateway processing.
Two types of gateway failures can occur:
v Failure of a first-hop gateway. A first-hop gateway is the gateway that is
specified in an IP route. First-hop gateways must be on a directly-connected
network. This type of failure can be detected by either TCP or the data link
layer.
v Failure of a gateway other than the first-hop gateway. The path between source
and destination TCP/IP hosts can traverse multiple gateways. This type of
failure can be detected only by TCP.
Dead gateway processing is initiated when IP receives a negative advice indicator
from either TCP or the data link layer. These indicators from TCP and the data link
layer are referred to as advice since they may result from transient conditions as
well as from a serious gateway failure.
Negative Advice from TCP or the Data Link Layer
Retransmissions on a TCP connection occur as a result of transient or non-transient
problems somewhere along the path to a destination host. When TCP notices
excessive retransmissions on a TCP connection, a TCP negative advice indicator is
sent to IP.
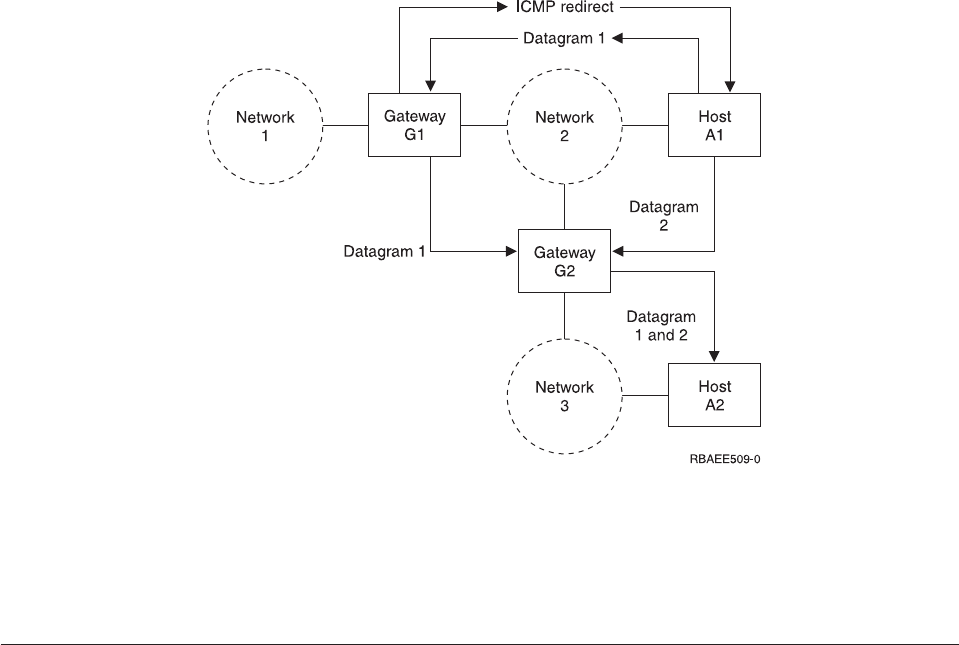
Figure 46. Example of ICMP Redirect
Chapter 2. TCP/IP: Operation, Management, and Advanced Topics 55


















