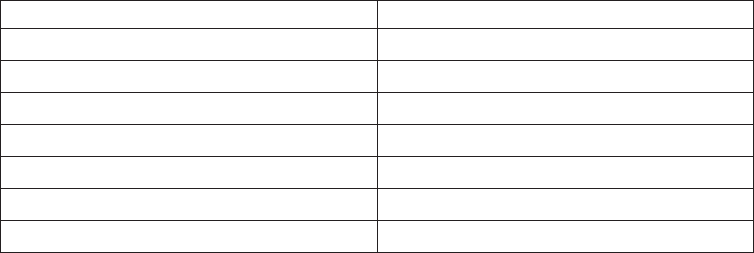
The following table shows which type of services your server uses for some of the
TCP/IP applications:
Table 6. AS/400 TCP/IP applications and Type of Services
Protocol or Application Type of Service Used
TELNET Normal
FTP (control connection) Minimize delay
FTP (data connection) Maximize throughput
SMTP (command phase) Minimize delay
SMTP (data phase) Maximize throughput
POP (all phases) Maximize throughput
SNMP Maximize reliability
Thus, TOS is a suggestion, not a demand, to the interface (if more than one is
present in the system) and to the routing algorithms. If a TCP/IP subsystem knows
more than one interface and more than one possible route to a given destination, it
uses the TOS to select one with characteristics closest to that desired.
TOS Example
For example, suppose the system can select between a low-capacity nonswitched
line or a high-bandwidth (but high delay) satellite connection:
v Datagrams carrying keystrokes from a user to a remote computer could have the
type of service set to *MINDELAY, requesting that they be delivered as quickly
as possible.
v Datagrams carrying a bulk file transfer could have the type of service set to
*MAXTHRPUT, requesting that they travel across the high-capacity satellite
path.
It is up to the network administrator to define TOS values when defining
interfaces and routes in the TCP/IP configuration. Based on the administrator’s
knowledge of the hardware technologies available on systems and networks used,
TOS values for the routes must also be defined according to the interface’sTOS
value. This means that if a *MINDELAY value is defined in the interface definition,
at least one route definition must have the *MINDELAY TOS value defined.
Note: A TCP/IP network does not guarantee the TOS requested. However,
datagram transmission is never denied.
Multiple Routes
You can have multiple routes in your routing table (by using the ADDTCPRTE
command). You can have more than one route for the same destination Internet
address with the same type of service or a different type of service. If you have
multiple routes with the same types of service, they are used in the order specified.
If a particular next hop router is not available, the subsequent specified next hop
router is used. This continues until an entry that is active is found or the list of
next hop values is exhausted. If you have multiple routes with different TOS, the
one with the TOS equal to the one requested by applications with TOS octet in IP
datagram is used. If no match is found in any specified routes, the route with the
closest TOS or *NORMAL TOS is used.
You can have *DFTROUTE, and specific route destination addresses. Default routes
are used only when data is sent to a remote destination system that does not have
Chapter 2. TCP/IP: Operation, Management, and Advanced Topics 61


















