26 536EX Chipset Developer’s Manual
Intel Confidential
Data Mode AT COMMANDS
Data Mode AT COMMANDS 3
The 536EX chipsets implement:
• Standard Hayes*-compatible AT commands and S-registers in data mode
• Standard EIA/TIA-578 AT commands in Class 1 fax mode
• Additional AT command sets for error correction, data compression and voice mode
In data mode, the AT commands configure the DCE (modem) to establish a connection with a
remote data modem. In data mode, the 536EX chipsets execute the AT commands for error
correction (MNP 2-4, V.42) and data compression (MNP 5, V.42 bis) described in Table 21 on
page 57, as well as the fax and voice mode commands AT+FCLASS=1 (fax) and AT+FCLASS=8
(voice).
3.1 Using AT Commands to Access the S-Registers
[Sn?, Sn=x, ?]
The DTE can access the S-registers through the ATSn?, ATSn=x, and ? commands. For example,
to configure the modem to automatically answer a data modem call after two rings, type ATS0=2.
Examples:
ATS0=2 Configures S-register S0 to ‘2’
ATS0? Reads the contents of S-register S0
ATS0= Configures S-register S0 to ‘0’
AT? Reads the contents of the last accessed (read or write) S-register
3.2 Modem Responses and Command Echo [En, Vn, Xn,
Wn, Qn]
The ATEn command configures the DCE to send back to the DTE any data that the DTE sent to
the DCE while in command mode. The ATVn command sets the DCE response codes to either text
or numeric form. For example, upon successfully processing an AT command string, the DCE
sends an ‘OK’ (text) or a ‘0’ (numeric) to the DTE.
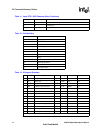
Examples:
Modem Setup
Host
Command
Modem Response
Echo, Numeric (E1, V0) AT<CR> AT<CR>0<CR>
ATS0?<CR> ATS0?<CR>000<CR><LF>0<CR>
Echo, Text (E1, V1) AT<CR> AT<CR><CR><LF> OK<CR><LF>
ATS0?<CR> ATS0?<CR><CR><LF>000<CR><LF><CR>
<LF>OK<CR><LF>