•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
FPC Installation Instructions
19
Replace an FPC in an M40e or M160 Router
4. Grasp the front of the FPC with one hand and place the other hand under the FPC to
support it.
5. Align the rear bottom corners of the FPC with the guides at the bottom of the desired
FPC slot. Slide the FPC all the way into the card cage until it contacts the midplane.
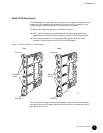
6. Push the ends of the ejector levers inward until they are nearly flush with the face of the
FPC (see Figure 12, which shows an M160 router).
7. If installing an M40e-FPC1 or M40e-FPC2 in an M40e router or any FPC in an
M160 router, you can remove or replace PICs at this point. For instructions, see the
M40e Internet Router Hardware Guide or M160 Internet Router Hardware Guide.
8. If any of the PICs on the FPC connect to fiber-optic cable, remove the rubber safety cap
from each transceiver and cable.
9. Insert the appropriate cable into the cable connector ports on each PIC on the FPC.
Secure the cables so that they are not supporting their own weight. Place excess cable
out of the way in a neatly coiled loop, using the cable management system. Placing
fasteners on a loop helps to maintain its shape.
10. Press and hold the FPC offline button on the craft interface above the slot that houses
the FPC to bring the FPC and PICs online. When the FPC is online, the FPC LED labeled
OK on the craft interface lights steadily and you can release the offline button.
Do not hold the FPC by the ejector levers, bus bars, or edge
connectors. They cannot support its weight.
When an M40e-FPC is installed in the chassis, the lettering
on the faceplates of the PICs is upside down .
Do not look directly into the ends of fiber-optic cables or
into the transceivers on the PIC faceplate. Single-mode
fiber-optic cable and the PICs that use it (such as ATM and
SONET/SDH interfaces) emit laser light that can damage
your eyes.
Do not let cable hang free from the connector. Do not
allow fastened loops of cable to dangle from the ladder
rack, because this stresses the cable at the fastening point.
Avoid bending fiber-optic cable beyond its minimum bend
radius. An arc smaller than a few inches in diameter can
damage the cable and cause problems that are difficult to
diagnose.