PCI-2513 User's Guide Functional Details
16
The ability to scan digital and counter channels along with analog channels provides for a more deterministic
collection of data.
Bus mastering DMA
The PCI-2513 supports bus mastering DMA. With multiple DMA channels, analog, digital, and counter input
data, as well as digital output data, can flow between the PC and the PCI-2513 without consuming valuable
CPU time. The driver supplied with the PCI-2513 automatically uses bus mastering DMA to efficiently conduct
I/O from the PC to the PCI-2513.
Analog input
The PCI-2513 has a 16-bit, 1-MHz A/D coupled with 16 single-ended, or eight differential analog inputs. Seven
software programmable ranges provide inputs from ±10 V to ±100 mV full scale.
Analog input scanning
The PCI-2513 has several scanning modes to address various applications. You can load the 512-location scan
buffer with any combination of analog input channels. All analog input channels in the scan buffer are measured
sequentially at 1 µs per channel.
For example, in the fastest mode, with a 0 delay between the end of scan and the start of scan, a single analog
channel can be scanned continuously at 1 MS/s; two analog channels can be scanned at 500 kS/s each; 16
analog input channels can be scanned at 62.5 kS/s.
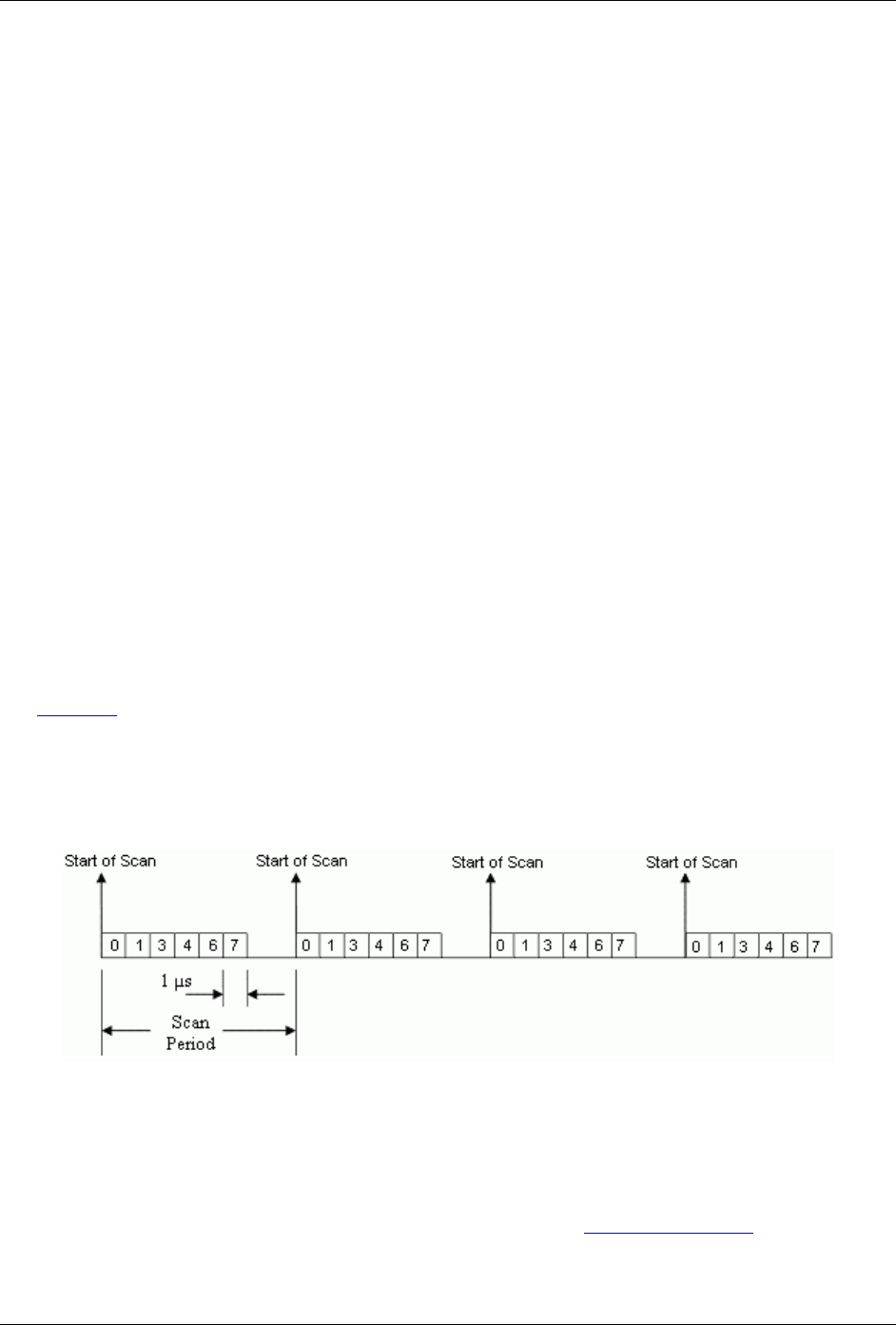
Example: Analog channel scanning of voltage inputs
Figure 4-2
shows a simple acquisition. The scan is programmed pre-acquisition and is made up of six analog
channels (Ch0, Ch1, Ch3, Ch4, Ch6, Ch7). Each of these analog channels can have a different gain. The
acquisition is triggered and the samples stream to the PC via DMA. Each analog channel requires one
microsecond of scan time—therefore the scan period can be no shorter than 6 µs for this example. The scan
period can be made much longer than 6 µs—up to 1 s. The maximum scan frequency is one divided by 6 µs or
166,666 Hz.
Figure 4-2. Analog channel scan of voltage inputs example
Digital I/O
Twenty-four TTL-level digital I/O lines are included in each PCI-2513. You can program digital I/O in 8-bit
groups as either inputs or outputs and scan them in several modes (see "Digital input scanning
" on page 17).
You can access input ports asynchronously from the PC at any time, including when a scanned acquisition is
occurring.