EDS-408A/405A Series User’s Manual Featured Functions
3-34
Using Virtual LAN
Setting up Virtual LANs (VLANs) on your EDS increases the efficiency of your network by
dividing the LAN into logical segments, as opposed to physical segments. In general, VLANs are
easier to manage.
The Concept of Virtual LAN (VLAN)
What is a VLAN?
A VLAN is a group of devices that can be located anywhere on a network, but which
communicate as if they are on the same physical segment. With VLANs, you can segment your
network without being restricted by physical connections—a limitation of traditional network
design. As an example, with VLANs you can segment your network according to:
y Departmental groups—You could have one VLAN for the Marketing department, another
for the Finance department, and another for the Development department.
y Hierarchical groups—You could have one VLAN for directors, another for managers, and
another for general staff.
y Usage groups—You could have one VLAN for e-mail users, and another for multimedia
users.
Benefits of VLANs
The main benefit of VLANs is that they provide a network segmentation system that is far more
flexible than traditional networks. Using VLANs also provides you with three other benefits:
y VLANs ease the relocation of devices on networks: With traditional networks, network
administrators spend much of their time dealing with moves and changes. If users move to a
different subnetwork, the addresses of each host must be updated manually. With a VLAN
setup, if a host on VLAN Marketing, for example, is moved to a port in another part of the
network, and retains its original subnet membership, you only need to specify that the new
port is on VLAN Marketing. You do not need to carry out any re-cabling.
1 2
3 4
5 6
7 8
1 2
3 4
5 6
7 8
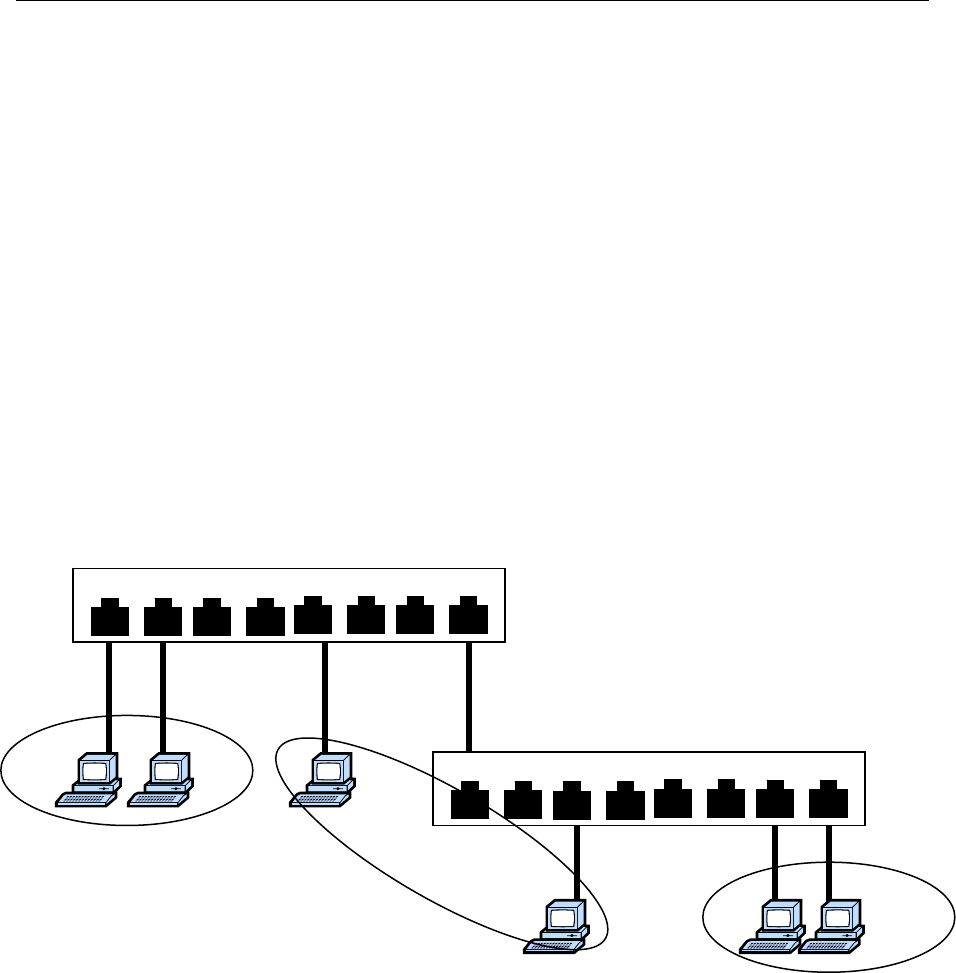
Switch
A
Switch B
Backbone connects multiple switches
Department 1
VLAN 1
Department 2
VLAN 2
Department 3
VLAN 3


















