Chapter 2 Function Generator Operation
©
National Instruments Corporation 2-3 NI 5401 User Manual
Direct Digital Synthesis (DDS)
Direct digital synthesis (DDS) is a technique for deriving, under digital
control, an analog frequency source from a single reference clock
frequency. This technique produces high-frequency accuracy and
resolution, temperature stability, wideband tuning, and rapid and
phase-continuous frequency switching.
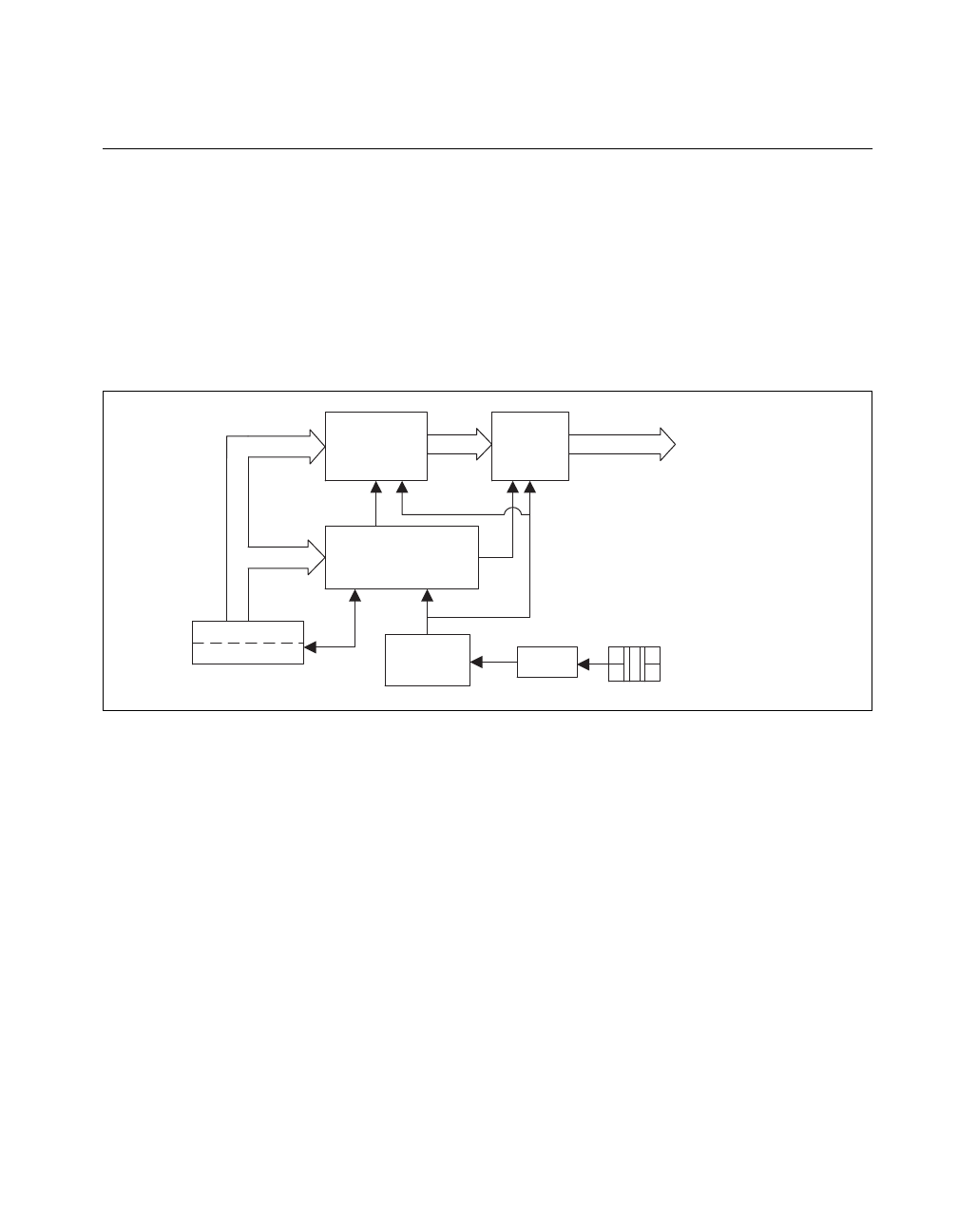
The NI 5401 uses a 32-bit, high-speed accumulator with a lookup memory
and a 12-bit DAC for DDS-based waveform generation. Figure 2-3 shows
the building blocks for DDS-based waveform generation.
Figure 2-3.
DDS Building Blocks
The lookup memory is dedicated to the DDS. You can store one cycle of a
repetitive waveform—a sine, triangular, square, or arbitrary wave—in the
lookup memory. Then, you can change the frequency of that waveform by
sending just one instruction. You can use DDS mode for very fine
frequency resolution function generation. You can generate sine waves of
up to 16 MHz with the NI 5401. Waveform generation always loops back
to the beginning of the lookup memory after passing through the end of the
lookup memory.
The NI 5401 uses a lookup waveform memory for storing the waveform
buffer and FIFO memory for storing the staging list, which contains
multiple frequency list information. This FIFO is referred to as an
instruction FIFO.
80 MHz Oscillator
Div/2
16-Bit
Counter
Sequencer
Instruction FIFO
Frequency
Time
Data Out (16)
DDS
Time
Frequency
Lookup
Memory
(14)