253
Data Link I/O Response Time Section 8-3
The number of bytes in each message differs according to the instruction
being issued.
Calculation Example Communications conditions are as follows:
Transmission medium: Twisted-pair cables
Baud rate: 2 Mbps
Network parameters: Defaults
Max node address: 32
Polled nodes per comm cycle: 4
Event-frames per comm cycle: 35
Network configuration: 8 nodes
Nodes that send messages: 2 nodes
Bytes in all messages sent: 2,012
× 2 bytes
In this example, B to E in the equation have the following values.
B: 4
C: 8
D: 2
E: 4,024
The communications cycle time is thus as follows:
600
× 4 + 110 × 8 + 320 × 2 + 4 × 4,024 + 2,290 = 22,306 (µs)
≅ 22 (ms)
8-3 Data Link I/O Response Time
When accurate communications timing is required, you need to understand
data exchange timing and the time required for data transmission and recep-
tion via data links. Use the information described in this section as reference
information for system construction.
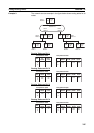
8-3-1 Data Exchange Timing
This section describes data exchange timing for data links between the Con-
troller Link Unit and the PLC’s CPU Unit. Data exchange is executed as inter-
rupt processing during CPU Bus Unit or Programming Device/Host Link
servicing performed by the CPU Unit. This interrupt processing is executed
each time data exchange between the local node and each node connected
via a data link is completed.
Data exchange timing differs depending on the CPU Unit model and the CPU
Unit the Execute Process (asynchronous or synchronous) specified in PLC
Setup, as described below.
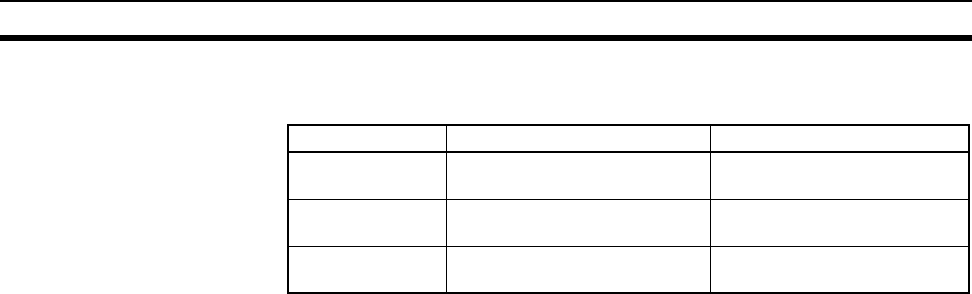
Instruction When sent When received
SEND Number of words to be sent × 2
+ 18
14
RECV 18 Number of words to be
received × 2 + 14
CMND Number of bytes in command
data + 10
Number of bytes in response
data