High Performance Two Port 10/100 Managed Ethernet Switch with 32-Bit Non-PCI CPU Interface
Datasheet
Revision 1.4 (08-19-08) 132 SMSC LAN9312
DATASHEET
9.9 RX Data Path Operation
When an Ethernet Packet is received, the Host MAC Interface Layer (MIL) first begins to transfer the
RX data. This data is loaded into the RX Data FIFO. The RX Data FIFO pointers are updated as data
is written into the FIFO.
The last transfer from the MIL is the RX status word. The LAN9312 implements a separate FIFO for
the RX status words. The total available RX data and status queued in the RX FIFO can be read from
the RX FIFO Information Register (RX_FIFO_INF). The host may read any number of available RX
status words before reading the RX Data FIFO.
The host must use caution when reading the RX data and status. The host must never read more data
than what is available in the FIFO’s. If this is attempted an underrun condition will occur. If this error
occurs, the Ethernet controller will assert the Receiver Error (RXE) interrupt. If an underrun condition
occurs, a soft reset is required to regain host synchronization.
A configurable beginning offset is supported in the LAN9312. The RX data Offset field in the Receive
Configuration Register (RX_CFG) controls the number of bytes that the beginning of the RX data buffer
is shifted. The host can set an offset from 0-31 bytes. The offset may be changed in between RX
packets, but it must not be changed during an RX packet read.
The LAN9312 can be programmed to add padding at the end of a receive packet in the event that the
end of the packet does not align with the host burst boundary. This feature is necessary when the
LAN9312 is operating in a system that always performs multi-DWORD bursts. In such cases the
LAN9312 must guarantee that it can transfer data in multiples of the Burst length regardless of the
actual packet length. When configured to do so, the LAN9312 will add extra data at the end of the
packet to allow the host to perform the necessary number of reads so that the Burst length is not cut
short. Once a packet has been padded by the H/W, it is the responsibility of the host to interrogate the
packet length field in the RX status and determine how much padding to discard at the end of the
packet.
It is possible to read multiple packets out of the RX Data FIFO in one continuous stream. It should be
noted that the programmed Offset and Padding will be added to each individual packet in the stream,
since packet boundaries are maintained.
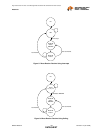
9.9.1 RX Slave PIO Operation
Using PIO mode, the host can either implement a polling or interrupt scheme to empty the received
packet out of the RX Data FIFO. The host will remain in the idle state until it receives an indication
(interrupt or polling) that data is available in the RX Data FIFO. The host will then read the RX Status
FIFO to get the packet status, which will contain the packet length and any other status information.
The host should perform the proper number of reads, as indicated by the packet length plus the start
offset
and the amount of optional padding added to the end of the frame, from the RX Data FIFO. A
typical host receive routine using interrupts can be seen in Figure 9.7, while a typical host receive
routine using polling can be seen in Figure 9.8.