Appendix B: Understanding RAID ● 76
RAID 6 Arrays
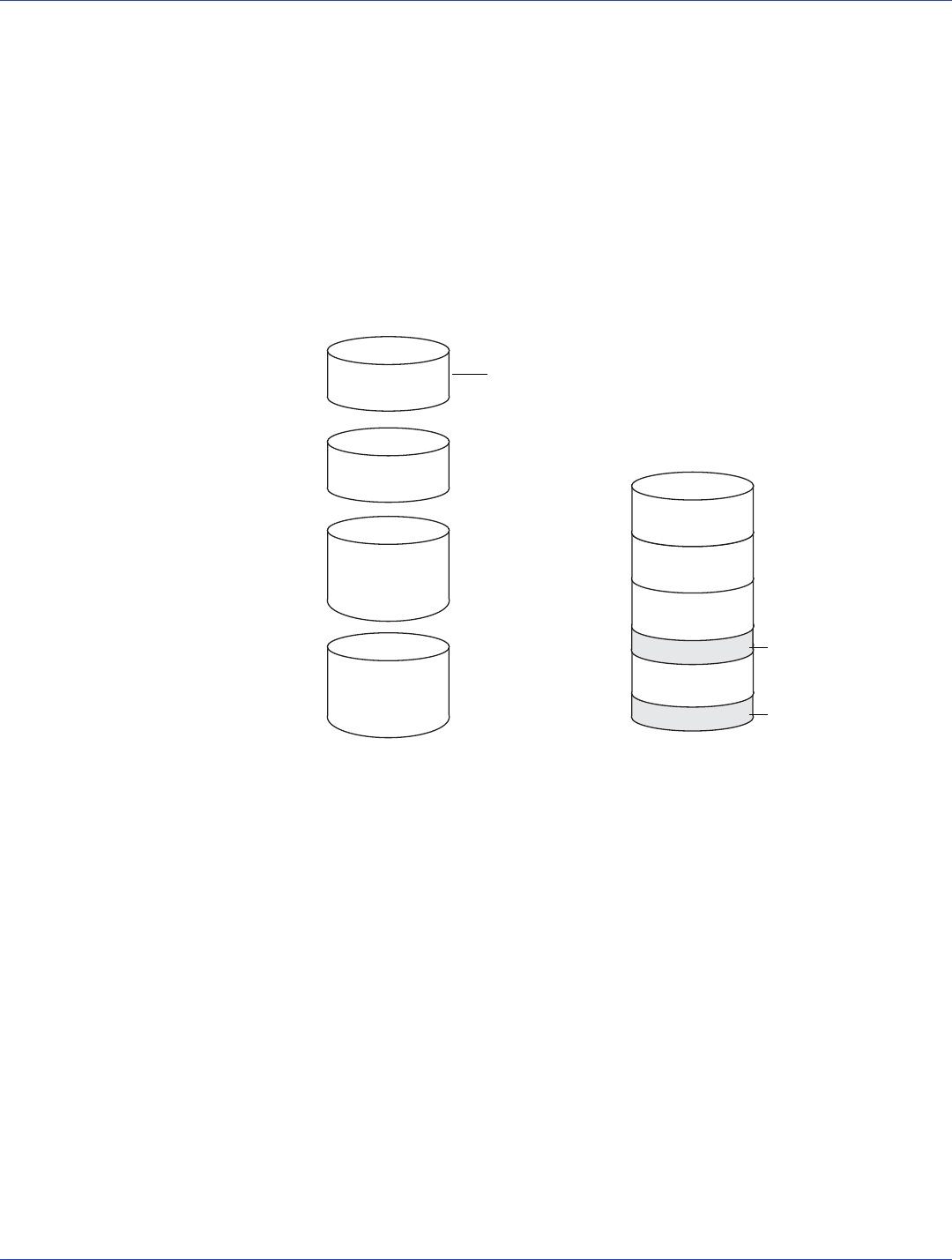
A RAID 6 array—also known as dual drive failure protection—is similar to a RAID 5 array
because it uses data striping and parity data to provide redundancy. However, RAID 6 arrays
include two independent sets of parity data instead of one. Both sets of parity data are striped
separately across all disk drives in the array.
RAID 6 arrays provide extra protection for your data because they can recover from two
simultaneous disk drive failures. However, the extra parity calculation slows performance
(compared to RAID 5 arrays).
RAID 6 arrays must be built from at least four disk drives. Maximum stripe size depends on
the number of disk drives in the array.
RAID 60 Arrays
Similar to a RAID 50 array (see page 75), a RAID 60 array—also known as dual drive failure
protection—is built from eight disk drives configured as two or more RAID 6 arrays, and
stripes stored data and two sets of parity data across all disk drives in both RAID 6 arrays.
Note:
Because they support four disk drives only, the Adaptec 2420SA RAID controller can’t
support RAID 60 arrays.
Two sets of parity data provide enhanced data protection, and striping improves performance.
RAID 60 arrays also provide high data transfer speeds.
Disk Drive 1
Disk Drive 2
Disk Drive 3
Disk Drive 4
250 GB
250 GB
400 GB
400 GB
Drive Segment Size
(Smallest Disk Drive)
Disk Drive 2
Disk Drive 3
Disk Drive 4
Disk Drive 1
1 P1 ... P2
2 P2 ... 449
P1 3 ... P1
P2 4 ... 500
Unused Space = 150 GB
Disk Drives in Logical Drive Based on the drive segment sizes used:
RAID 6 Logical Drive = 500 GB plus
parity (P1 & P2)
Unused Space = 150 GB


















