Configuring Spanning Tree
Configuring Classic Spanning Tree
Page 91
Defining STP Interfaces
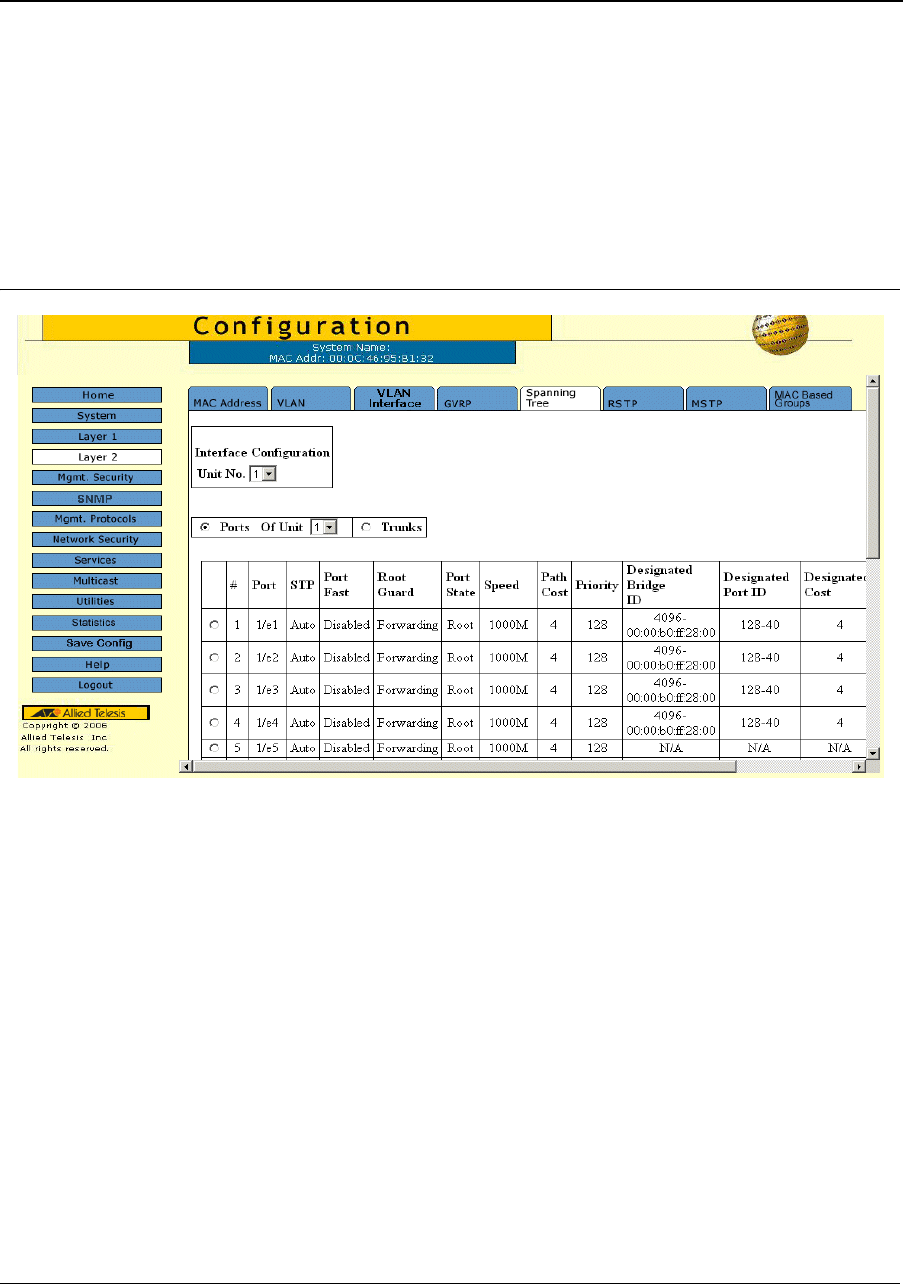
Network administrators can assign STP settings to a specific interface (port or LAG) using the STP Interface
Configuration Page. The Global LAGs section displays the STP information for Link Aggregated Groups.
To assign STP settings to an interface (port or LAG):
1. Click Layer 2 > Spanning Tree. The Spanning Tree Page opens.
2. Click Configure. The STP Interface Configuration Page opens:
Figure 55: STP Interface Configuration Page
The STP Interface Configuration Page contains the following sections:
• Interface Configuration
• STP Port Parameters table
• Global System LAGs table
The parameters listed in both tables are identical.
The STP Interface Configuration Page contains the following fields:
• Unit Number — Indicates the stacking member for which the STP information is displayed.
• Port — Displays the port or LAG on which STP is enabled.
• STP Status — Indicates if STP is enabled on the port. The possible field values are:
– Enabled — Indicates that STP is enabled on the port.
– Disabled — Indicates that STP is disabled on the port.
• Port Fast — Indicates if Fast Link is enabled on the port. If Fast Link mode is enabled for a port, the Port
State is automatically placed in the Forwarding state when the port link is up. Fast Link optimizes the STP
protocol convergence. STP convergence can take 30-60 seconds in large networks.
• Root Guard — Prevents devices outside the network core from being assigned the spanning tree root.
• Port State — Displays the current STP state of a port. If enabled, the port state determines what forwarding
