126
Troubleshooting
Troubleshooting
127
section
2
1
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
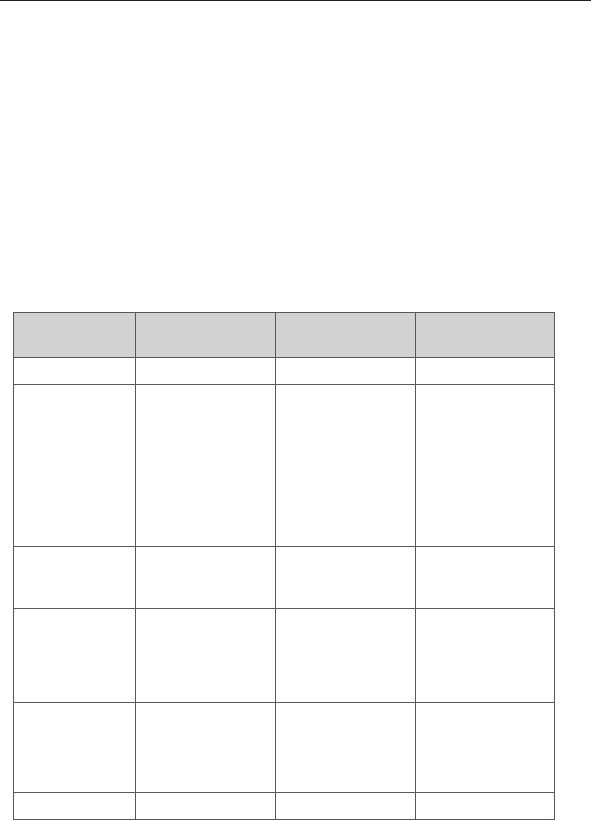
What’s the difference between 802.11b, 802.11g and 802.11a?
Currently there are three levels of wireless networking standards,
which transmit data at very different maximum speeds. Each is
based on the designation 802.11x, so named by the IEEE, the
board that is responsible for certifying networking standards. The
most common wireless networking standard, 802.11b, transmits
information at 11Mbps; 802.11a and 802.11g work at 54Mbps. See
the following chart for more detailed information.
Wireless Comparison
Wireless
Technology
802.11b 802.11g 802.11a
Speed 11Mbps 54Mbps 54Mbps
Frequency Common
household
devices such as
cordless phones
and microwave
ovens. May
interfere with
the 2.4GHz
unlicensed band
Common
household
devices such as
cordless phones
and microwave
ovens. May
interfere with
the 2.4GHz
unlicensed band
5GHz -
uncrowded band
Compatibility Compatible with
802.11g
Compatible with
802.11b
Incompatible
with 802.11b or
802.11g
Range Depends on
interference -
typically 50-300
ft. indoors
Depends on
interference -
typically 50–300
ft. indoors
Less interference
- range is
typically 50-100
feet
Adoption Mature - widely
adopted
Expected to
continue to grow
in popularity
Slow adoption
for consumers -
more popular in
business
Price Inexpensive More expensive Most expensive


















