3-5
Cisco PNNI Network Planning Guide for MGX and SES Products, Release 5
Part Number OL-3847-01 Rev. D0, April, 2004
Chapter 3 Address and Closed User Group Planning
Planning Address Configuration Settings
Guidelines for Selecting an Address Format
It is important to select a address format plan which meets the future needs and scale of the network.
Changing the node ATM address format and addresses after its initial deployment requires major service
disruption, and requires complete reconfiguration of the node and all of its connections. Consider the
following guidelines when selecting an address format:
• Consider whether a registered address will be required in the future. The default registered address
is registered to Cisco and is part of the ATM address.
• If an address format has been chosen for the WAN, or if your WAN will consist of existing nodes
for which an address format has been selected, you can select that address format.
• Both Public ATM networks (PSTNs) and Narrowband Integrated Services Digital Networks
(N-ISDN) usually use E.164 numbers. PNNI allows end-system reachability to be advertised via the
E.164 address prefix.
• In the Data Country Code (DCC) format, each country has a unique DCC value. If you select this
address format, your value must match this standard.
• In the International Code Designator (ICD) format, the ICD identifies an organization such as a
company or campus. This identification is useful when you are deploying a WAN that will be
accessed by several campuses or sites.
• Native E.164 addresses can be embedded in the AESA.
Enter the address format or formats that you select into the Nodal Address Worksheet, Table 3-4, which
appears at the end of this chapter.
Note Local AFIs should not be used for addressing within ATM Service Provider networks.
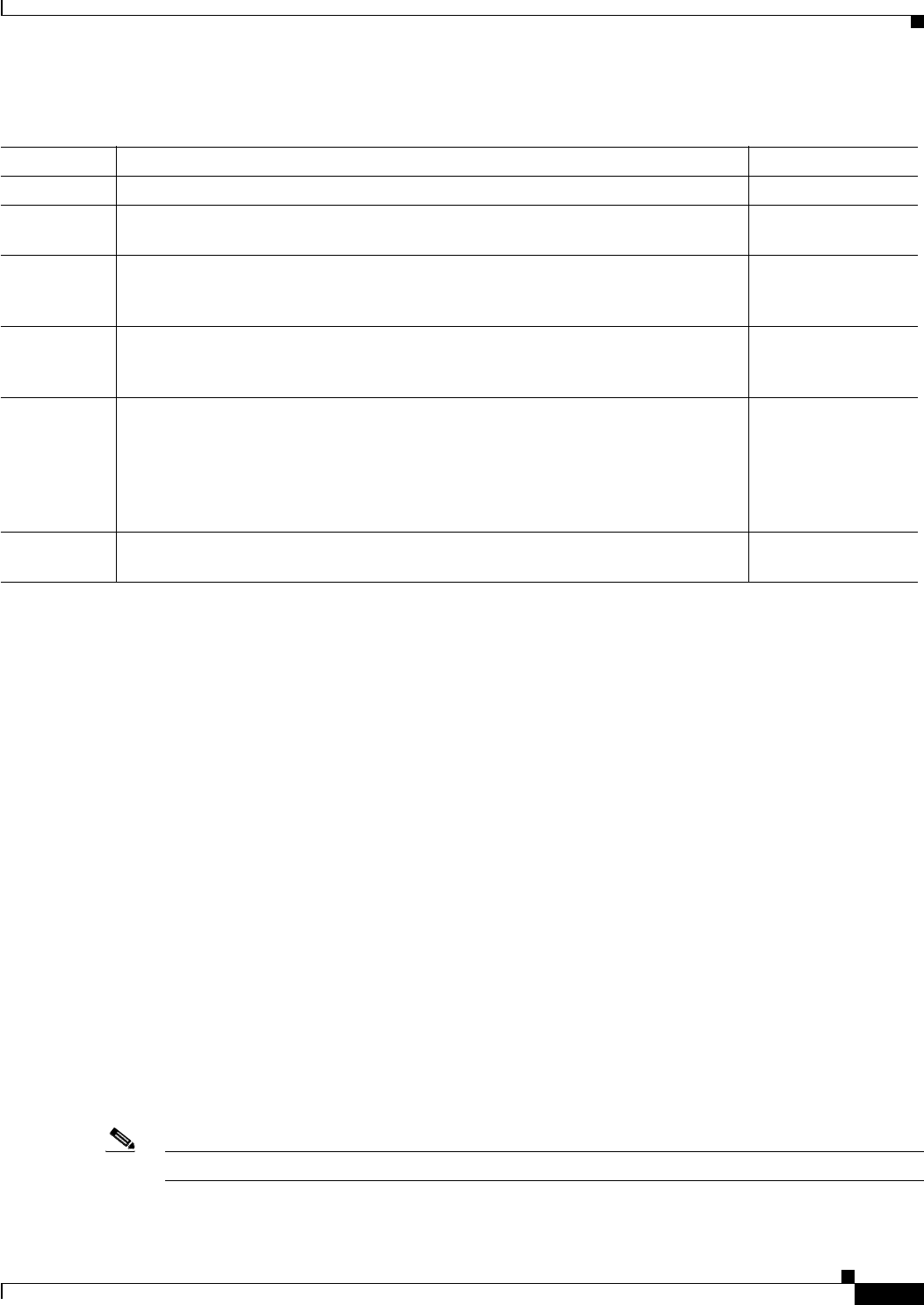
Table 3-1 ATM Address Components
ATM Field Description Default Values
AFI Authority Format Identifier (1 byte). 47
ICD International Code Designator (2 bytes) The default value is the ICD assigned to
Cisco Systems.
0091
IDI Initial Domain Identifier (8 bytes). The contents of this field vary depending on the
value of the AFI. For example, with a DCC AESA (AFI=39), the IDI value of Hex
840F identifies the United States.
—
HO-DSP High-Order Domain Specific Part (4 to 12 bytes). The meaning is defined by the
address authority controlling the AESA. This component couples with AFI and IDI
to route a call to the appropriate switch.
—
ESI End System Identifier (6 bytes). This field repeats the PNNI Controller MAC address
when the ATM address identifies the PNNI node. (When an ATM address identifies
an ATM end system, the ESI field will be completed through ILMI registration with
the end system. In this case, the ESI is typically the MAC address of the ATM CPE.
The unique ESI field will distinguish that ATM end system [ATM CPE] from all other
ATM end systems.)
PXM45
MAC address at first
boot.
SEL PNNI selector byte (1 byte). The selector byte is used to identify different target
applications on the node.
00


















