Configuring the Spanning Tree Protocol 721
MSTP with Multiple Forwarding Paths
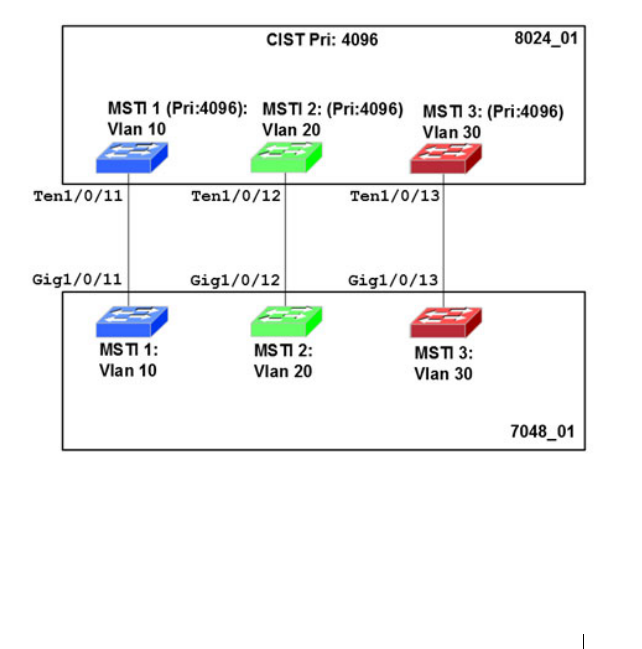
Consider the physical topology shown in Figure 22-4. It might be assumed
that MSTI 2 and MSTI 3 would follow the most direct path for VLANs 20
and 30. However, using the default path costs, this is not the case. MSTI
operates without considering the VLAN membership of the ports. This results
in unexpected behavior if the active topology of an MSTI depends on a port
that is not a member of the VLAN assigned to the MSTI and the port is
selected as root port. In this configuration, port TE 1/0/11 is selected as the
root port and ports TE1/0/12 and TE1/0/13 are blocked. To resolve the issue,
set the port path cost of the directly connected links to allow the MSTIs to
connect directly.
Figure 22-4. MSTP with Multiple Forwarding Paths


















